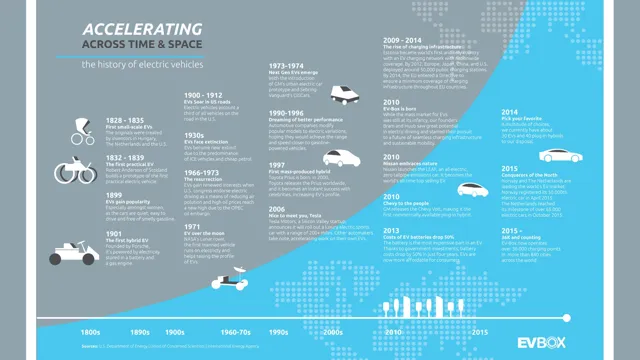
The Electrifying Journey: Tracing the History of Electric Cars
Electric cars are becoming increasingly popular as the world tries to reduce the carbon footprint and fight against climate change. These vehicles are powered by electric motors instead of gasoline engines, which emit harmful greenhouse gases into the atmosphere. However, the concept of electric cars is not new, and it dates back to the early 19th century.
In this blog post, we will delve into the history of electric cars and explore how they have evolved into what we see today. Join us on this journey as we take a deep dive into the past, present, and future of electric vehicles.
Early Inventions and Concepts
The history of electric cars can be traced back to the early days of automobiles. In fact, electric vehicles were quite popular in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. Some of the earliest inventors and pioneers of electric cars include Thomas Davenport and Robert Anderson.
However, it was the invention of the rechargeable lead-acid battery in the 1860s that really paved the way for widespread electric vehicle use. As the internal combustion engine became more dominant, electric cars gradually fell out of favor. It wasn’t until the oil crisis in the 1970s that interest in electric vehicles was reignited.
Since then, there have been many advancements in battery technology and electric motor design that have made electric cars more efficient, reliable, and affordable. And while they still only make up a small portion of the global automotive market, electric vehicles are poised to play a much bigger role in our transportation system in the coming years.
1832: The Birth of Electric Cars
In 1832, the first electric car was invented by Scottish inventor Robert Anderson. Although it looked nothing like the sleek electric cars we see today, the invention was groundbreaking nonetheless. Anderson’s creation consisted of non-rechargeable cells that powered a small electric motor which in turn drove the vehicle’s wheels.
It was more of a prototype than a practical car since it could only travel a few miles before the battery needed to be replaced, but it paved the way for further inventions and concepts within the electric car industry. In the following years, multiple inventors and engineers developed new electric car models. However, it wasn’t until the 1900s that electric cars became more practical and popular among the public.
Despite this, we can still appreciate the innovation and foresight of those early inventors who laid the foundation for the electric car industry that thrives today.

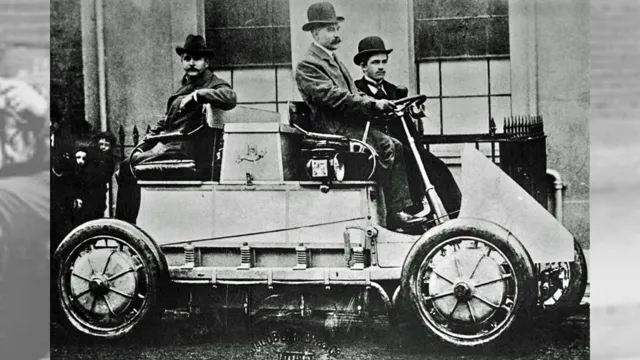
1859: The First Battery-powered Carriage
In 1859, French physicist Gaston Planté presented the world’s first battery-powered carriage. This invention was a remarkable achievement for its time and reflected a new era of electromobility that would later change the way we travel. Although Planté’s carriage could only run for a short distance, it paved the way for future innovations in the field of batteries and electric vehicles.
Early inventions like Planté’s electric carriage were crucial in shaping the future of transportation. Thanks to these early visions, we now have a diverse range of electric vehicles available and are moving closer towards a cleaner, more sustainable future. It is fascinating to think of the incredible technological advancements that have been made since 1859 and to imagine what the future holds for electric vehicles.
The Rise and Fall in Popularity
The history of electric cars shows an interesting rise and fall in popularity. Electric vehicles were actually quite popular in the 19th century before gasoline-powered cars became the norm. However, as the 20th century rolled along and the mass production of gasoline cars took off, electric cars slowly faded into obscurity.
It wasn’t until the late 1990s and early 2000s that electric cars made a comeback, with models like the Toyota Prius and Tesla Roadster garnering attention. Yet, even with advancements in battery technology and the push for sustainable transportation, electric cars still only account for a small percentage of cars on the road. However, with companies like Tesla continuing to innovate and other car manufacturers starting to follow suit, it’s possible that electric cars could take a greater role in the future of transportation.
1890s: The Golden Age of Electric Cars
In the late 1890s, electric cars were all the rage. Innovations in battery technology and the convenience of a car that was easy to drive and maintenance-free made them a desirable choice for early motorists. However, the high cost, limited range, and lack of infrastructure proved to be significant drawbacks.
As gasoline-powered cars became cheaper and more efficient, electric cars started to fade from popularity. By the 1920s, they were almost nonexistent. Today, electric cars are once again on the rise, but with improvements in technology, infrastructure, and environmental concerns, perhaps this time they’ll be here to stay.
The Golden Age of electric cars may be long gone, but its legacy lives on in the continued pursuit of clean and efficient transportation.
Early 1900s: The Dominance of Gasoline Cars
During the early 1900s, the dominance of gasoline cars was firmly established, with gasoline-powered vehicles accounting for over 90% of the automobile market. Gasoline engines were considered more reliable and easily accessible than other alternatives, such as steam-powered or electric cars, which required more specialized knowledge and equipment to operate and maintain. However, this dominance was not without challenges, as many people were concerned about the environmental impact of gasoline cars, particularly their contribution to air pollution and dependence on non-renewable resources.
In the coming decades, alternative fuels and more efficient engines would come to challenge the dominance of traditional gasoline-powered cars, leading to a shift in the automotive landscape. Nonetheless, the rise and fall of gasoline cars serve as a reminder of the importance of innovation and adaptation in any industry.
Modern Advancements and Comeback
Electric cars have been around for over a century, but it is only in recent years that they have gained popularity and become a viable alternative to traditional gasoline-powered vehicles. In the early days of the automobile, electric cars were actually more common than gasoline ones. However, advances in technology and the discovery of oil reserves led to gasoline becoming the preferred fuel source.
In the 1990s, electric cars made a comeback with the development of more efficient batteries, but they still faced some challenges, such as limited range and high costs. However, in the past decade, electric cars have seen a rapid surge in popularity and advancements in technology have made them more accessible and affordable than ever before. With the increasing concerns about climate change and the need for sustainable transportation, it is clear that the history of the electric car is far from over.
1990s: The Reintroduction of Electric Cars
The 90s marked the reintroduction of electric cars, and we’ve come a long way since then. Thanks to technological advancements, electric cars have made a massive comeback, with several luxury and affordable options available. The modern-day electric car comes with cutting-edge features such as regenerative braking, fast charging, improved battery life, and advanced safety systems.
The Tesla Model S is one of the most popular electric cars of the decade, rightly earning the title of the world’s best-selling electric vehicle. Other notable electric cars include the Nissan Leaf and the Chevrolet Bolt. Electric cars have many benefits, including zero-emission of carbon emissions, fuel savings, and in some cases, tax incentives.
With innovative features and environmental benefits, electric cars promise a bright future for the automotive industry.
Current Innovations in Electric Car Technology
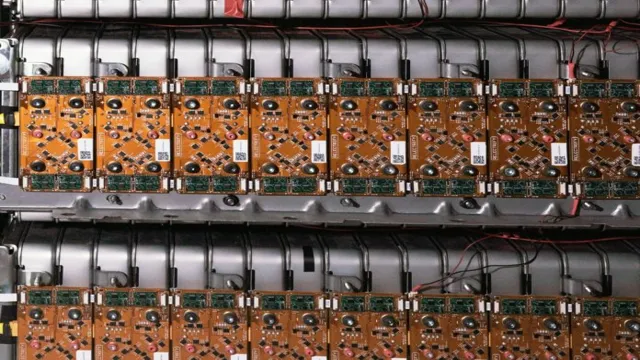
Electric car technology has come a long way since its initial development in the 19th century. In recent years, there has been a surge in innovative technologies that aim to make electric cars more efficient, sustainable, and affordable. One of the most notable advancements is the use of solid-state batteries, which offer a higher energy density and are safer to use than traditional batteries.
Another promising development is the use of wireless charging, which enables electric vehicles to charge while on the move, offering greater convenience to drivers. Furthermore, the automotive industry is working towards reducing the environmental impact of electric cars by using sustainable materials and designing vehicles for increased recyclability. As a result of these modern advancements, electric cars are rapidly becoming a more viable option for consumers, paving the way for a greener and more sustainable future.
Looking Ahead to the Future
As we look towards the future of transportation, it’s hard not to reflect on the history of electric cars. These vehicles have been around for over a century, starting with early experiments in battery-powered vehicles that emerged in the late 1800s. While they never quite gained the same popularity as their gas-powered counterparts, they’ve remained a somewhat niche but increasingly important part of the automotive landscape.
In recent years, advancements in battery and charging technology, as well as concerns about climate change, have given electric cars renewed attention and interest. Indeed, some experts predict that they will soon become mainstream, with electric vehicles eventually replacing fossil-fuel-powered cars entirely. Regardless of how the future shakes out, there’s no doubt that the history of the electric car offers an interesting and important perspective on the evolution of transportation and the role of sustainable technology in our lives.
Conclusion
From the early experimentation with batteries and electric motors in the 19th century to the modern-day electric cars, the history of electric vehicles has been nothing short of electrifying. Though they faced many challenges and setbacks, including the rise of gasoline-powered cars and battery limitations, electric cars have proven to be a formidable competitor in the automotive industry. With the world’s rapidly increasing need for sustainable transportation solutions, electric cars are finally getting the recognition they deserve and are poised to play a pivotal role in shaping the future of transportation.
So, let’s buckle up and ride into this exciting electric future towards a cleaner, greener and brighter tomorrow!”
FAQs
What is the history of electric cars?
Electric cars have a long and storied history, dating back to the early 19th century and the invention of the first electric vehicle by Scottish inventor Robert Anderson in 1832. Over the years, electric cars have undergone a number of technological advancements and have become an increasingly viable alternative to traditional gasoline-powered vehicles.
When did electric cars become popular?
Electric cars were first popularized in the late 1800s and early 1900s, as cities across the world began to adopt electric streetcars and buses. However, their popularity waned in the mid-20th century as advances in gasoline engine technology made traditional cars more affordable and practical.
What are the benefits of electric cars?
The benefits of electric cars are many, including lower emissions, reduced fuel costs, and increased energy efficiency. Additionally, electric cars require less maintenance than traditional gasoline-powered vehicles, as they have fewer moving parts and don’t require regular oil changes.
How has electric vehicle technology evolved over time?
Electric vehicle technology has evolved rapidly over the past few decades, with improvements in battery technology and charging infrastructure making electric cars more practical and affordable than ever before. In the coming years, the development of new technologies such as solid-state batteries and wireless charging is likely to further revolutionize the electric vehicle industry.