Revving Up Your Knowledge: Exploring the Science Behind Electric Car Batteries
Electric cars are becoming more and more popular in today’s world, and it’s clear to see why. They’re eco-friendly, cost-effective, and sleek in design. But for some, the concept of electric car batteries can be somewhat confusing.
How do they work? What kind of maintenance is required? In this blog, we’ll dive into the world of electric car batteries to help you better understand the technology that powers these futuristic vehicles. We’ll discuss the types of batteries used, how they’re charged, and the benefits and drawbacks of each. So buckle up and get ready to learn about the inner workings of one of the most important components of electric cars.
What are electric car batteries?
Electric car batteries are power storage units that secure and deliver energy to electric motors, allowing them to generate motion. Contrary to traditional cars that rely on fossil fuels, electric cars use electricity stored in batteries, which are rechargeable. Electric car batteries use chemical reactions to generate electricity by converting stored energy into usable electricity that can be dispatched to the car’s electric motor to generate motion.
The batteries are composed of multiple cells, each containing a cathode, an anode, and electrolytes that act as a mediator and separator of ions. The cathode is made from metal oxide, the anode is made of graphite, and the electrolytes are lithium salts that enable the movement of ions between the cathode and anode. The electrical flow between them generates electrical energy, which is stored for use by the electric motor.
However, battery technology is constantly evolving, resulting in significant changes in electric vehicle range, lifespan, charging time, and cost.
The basic components
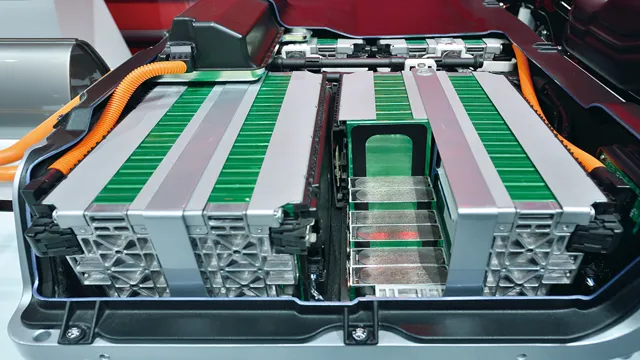
Electric car batteries are essential components that power electric vehicles. They differ from traditional car batteries because they require a higher voltage and energy density to ensure that the vehicle has enough power to travel. Most electric car batteries are made up of lithium-ion cells, which work together to store energy and deliver power to the vehicle’s electric motor.
These cells are arranged into modules, and the modules are then combined to form a battery pack that delivers the necessary voltage and energy to power the vehicle. The size and capacity of the battery pack vary depending on the type of electric vehicle and the manufacturer, but they typically have a range of 100 to 300 miles on a single charge. Electric car batteries are a crucial element of a sustainable future, providing a clean and efficient alternative to traditional fossil fuel-powered vehicles.
Types of electric car batteries
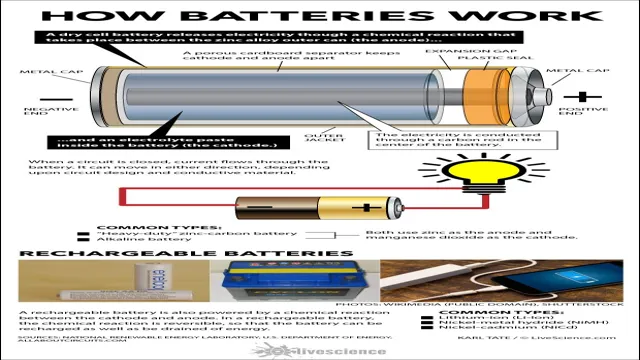
Electric car batteries come in different types, and each one has unique characteristics that make them suitable for different driving needs. The most common types of electric car batteries are lithium-ion (Li-ion) batteries and Nickel-metal Hydride (NiMH) batteries. Li-ion batteries are the most popular and widely used type of battery in electric cars due to their high energy density, longer lifespan, and fast-charging capabilities.
NiMH batteries, on the other hand, have been gradually phased out in favor of Li-ion batteries due to their lower energy density and shorter lifespan. Another type of electric car battery is the Solid State Battery, which is still in its early development phase. Solid-state batteries have the potential to revolutionize the electric vehicle industry by providing greater range, longer lifespan, and faster charging.
However, they are still expensive and not yet widely available. Overall, the type of battery used in an electric car plays a critical role in determining the car’s overall performance and range. Understanding the different types of electric car batteries is, therefore, essential for anyone looking to buy or own an electric car.
How do electric car batteries work?
Electric car batteries are an essential component of modern electric vehicles. These batteries use rechargeable lithium-ion cells to store electrical energy, which is then used to power the car’s electric motor. The batteries are typically sandwiched between the vehicle’s undercarriage and its body, keeping them out of sight but easily accessible.
When the driver accelerates or brakes, the battery sends a current to the motor, which converts the electrical energy into motion. The process is incredibly efficient, with many electric cars achieving upwards of 100 miles per charge, and some models even boasting a range of more than 300 miles before needing to plug in. When it’s time to recharge, the vehicle is simply plugged into a charging station, with most models able to fully charge within just a few hours.
Overall, electric car batteries are an exciting and innovative technology that’s changing the way we think about transportation and helping to reduce our carbon footprint.
Charging and discharging
Electric car batteries work by charging and discharging. When an electric car is plugged in, the battery is charged by electricity from an external power source, such as a charging station or an electrical outlet. Inside the battery, chemical reactions between the electrodes and the electrolyte store energy in the form of electric potential difference.
When the car is driven, the battery discharges, providing the electric current that powers the motor. The speed and range of the car depend on the battery’s capacity, which is measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh). The higher the capacity, the more energy the battery can store and the farther the car can travel on a single charge.
To optimize the lifespan and performance of a battery, it’s important to manage the charging and discharging properly. Just like a smartphone battery, it’s best to avoid overcharging or letting the battery drain completely. By using regenerative braking and intelligent charging algorithms, electric cars can extend their battery life and provide a seamless driving experience.
How does regenerative braking work?
How does regenerative braking work in electric cars? Regenerative braking is the process of using the electric motor in reverse to slow down the car and generate electricity at the same time. When you step on the brakes, the electric motor acts like a generator and converts some of the kinetic energy of the car into electrical energy, which is then stored in the battery. This helps the car to slow down and also saves energy that would otherwise be lost as heat during normal braking.
The amount of energy that is regenerated depends on factors such as the speed of the car, the weight of the vehicle, and how hard the brakes are applied. Overall, regenerative braking is an innovative way to make electric cars more energy-efficient and reduce their environmental impact.
Battery management system
Battery management system Electric car batteries function in a slightly different way compared to the batteries we use in our day-to-day life. These batteries are massive and can store an enormous amount of electricity, which is used to power the vehicle’s electric motor. The battery is managed by a battery management system (BMS), which regulates the flow of electricity to the motor and ensures that the batteries operate efficiently.
The BMS monitors the state of charge of each battery cell and makes sure that they are all functioning correctly. It also guarantees that the batteries don’t overcharge or discharge, thereby ensuring that the lifespan of the battery is extended. When the batteries are not under use, the BMS is responsible for keeping them in good condition by ensuring that they are stored at the optimum temperature.
As a result, an efficient BMS not only promotes battery longevity but also improves the electric car’s performance and range.
Advantages of electric car batteries
Electric car batteries utilize rechargeable lithium-ion cells to store energy, which power the vehicle’s electric motor. The batteries work by exchanging ions between the positive and negative electrodes, allowing electricity to flow from the battery to the motor or vice versa. One of the main advantages of electric car batteries is their efficiency, as they convert up to 85% of the energy stored into usable power, compared to the 20-30% efficiency of traditional combustion engines.
Additionally, electric car batteries have fewer moving parts, leading to a longer lifespan and reduced maintenance needs. They are also a more environmentally friendly option, as they produce zero emissions and can be charged using renewable energy sources. The batteries also provide a smoother and quieter driving experience due to the absence of vibrations and engine noise.
Overall, electric car batteries offer a multitude of benefits over traditional combustion engines, making them a popular option for environmentally conscious drivers looking for efficient and cost-effective transportation.
Cheaper to maintain
One of the advantages of electric car batteries is that they are cheaper to maintain than traditional combustion engines. With fewer moving parts, electric cars require less maintenance, reducing the overall cost of ownership. You won’t have to worry about oil changes, spark plug replacements, or other routine maintenance tasks typical of gas-powered vehicles.
Additionally, electric cars come with regenerative braking, meaning they recapture energy while braking, extending the life of their brakes. Electric car batteries typically last longer than gas-powered engines and are covered by lengthy warranties, giving you peace of mind and saving you money in the long run. Choosing an electric car battery not only saves you money but also reduces emissions, helping to preserve the environment.
So, if you’re in the market for a new car, why not consider switching to an electric vehicle and enjoy the cost savings and environmental benefits of electric car batteries?
Eco-friendly
Electric car batteries have numerous advantages over traditional gasoline-powered cars. For one, electric car batteries are eco-friendly and produce zero emissions. This means that they do not contribute to air pollution and carbon emissions, which is a significant problem today.
Additionally, electric car batteries are more fuel-efficient than traditional engines, which means that they can save you money in the long run on gas costs. Moreover, electric cars are quieter and smoother to drive, making for a more pleasant driving experience. While electric car batteries may have a higher upfront cost compared to gas-powered cars, they can provide significant savings over the car’s lifetime.
Therefore, the advantages of electric car batteries are not only beneficial for the environment, but they also provide cost savings and a more enjoyable driving experience. So if you’re considering purchasing a car, consider an electric car with its eco-friendly benefits and numerous advantages.
Conclusion
In conclusion, electric car batteries are marvels of modern engineering that allow us to power our vehicles with renewable energy sources. Think of them as tiny power plants that store and release electrons on demand, delivering the energy needed to propel a car forward. Their efficiency and longevity make them ideal for eco-friendly transport, and with the ongoing advancements in battery technology, who knows where they will take us next? It’s electrifying to imagine!”
FAQs
What type of batteries are used in electric cars?
Most electric cars use lithium-ion batteries to power their electric motors.
How long do electric car batteries last?
The lifespan of an electric car battery can vary, but typically they are designed to last for 8-10 years or 100,000-200,000 miles.
How do you charge an electric car battery?
Electric car batteries can be charged at home using a home charging station or a standard 120V electrical outlet, or at public charging stations.
How much energy can an electric car battery store?
The energy storage capacity of an electric car battery can vary, but typically ranges from 30-100 kilowatt-hours (kWh), which translates to a range of 100-300 miles on a single charge.