Revolutionizing Transportation: The Inner Workings of Gas and Electric Car Technology Explained
Gas Vs Electric Cars: Which is the Better Option? With the increasing concern for the environment, the debate on Gas Versus Electric Cars has never been more relevant. It’s no longer just a matter of personal preference or affordability, but now a matter of ethical responsibility towards the planet. While gas cars have been around for over a century and have dominated the market, electric cars have been gaining popularity in recent years.
However, both options have their pros and cons. In this blog post, we will explore the advantages and disadvantages of both gas and electric cars, and hopefully, help you determine which one is the better choice for you.
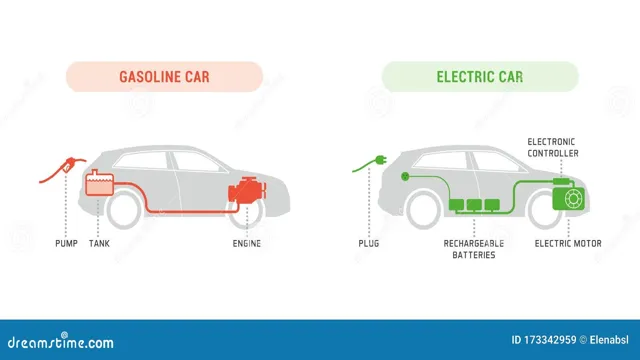
How Gas Cars Work
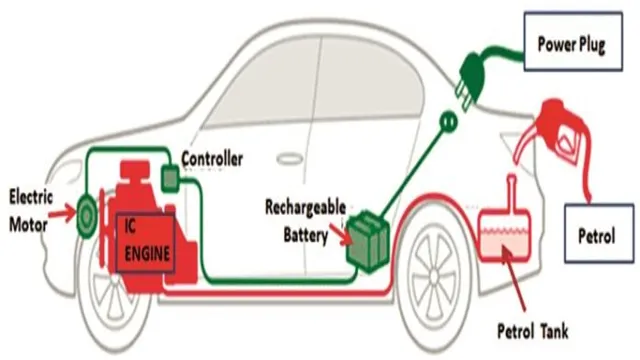
Gasoline-powered cars work by using an Internal Combustion Engine (ICE) that burns gasoline to create mechanical energy, which then powers the car. The engine mixes the gasoline with air and ignites this mixture using a spark from a spark plug. This causes a small explosion inside the engine that pushes a piston, which converts the energy from the explosion into rotational energy that ultimately drives the wheels.
The process is repeated hundreds of times each minute, creating a continuous flow of energy to the wheels. Gasoline cars can go long distances on a single tank of gas and can be refueled almost anywhere. However, they are not as fuel-efficient as electric cars and emit harmful gases into the environment.
With advancements in gas-electric car technology, hybrid cars now combine both gas and electric power, offering better fuel efficiency and lower emissions than traditional gas cars.
Internal Combustion Engine
Gas cars are powered by internal combustion engines, which are made up of several components that work together to create energy and propel the vehicle. The engine’s cylinders contain pistons that move up and down, compressing a mixture of air and gasoline into a small space. When a spark plug ignites the mixture, it explodes and rapidly expands, pushing the piston down and turning the crankshaft.
The crankshaft then transfers the energy to the transmission, which rotates the wheels and moves the car forward. This process happens continuously as long as there is fuel in the tank and the ignition system is functioning properly. While gasoline-powered cars have been the norm for decades, increased concern about carbon emissions has led to a growing interest in electric and hybrid vehicles.
However, internal combustion engines continue to be the primary power source in many forms of transportation, from cars and trucks to boats and airplanes.
Fuel Delivery System
The fuel delivery system is the heart of a gas car. It brings the fuel from the gas tank to the engine, where it is burned to produce the power needed to move the car. The fuel system includes a fuel pump, fuel filter, fuel injectors, and a fuel pressure regulator.
When you turn the key in the ignition, the fuel pump activates and sends fuel through the fuel filter and into the fuel injectors. The fuel pressure regulator ensures that the fuel pressure is consistent, allowing the injectors to spray a precise amount of fuel into each cylinder. The vaporized fuel mixes with air and is ignited by a spark from the spark plug, creating the controlled explosion that powers the engine.
Without a functioning fuel delivery system, your car won’t go anywhere. Remember to regularly maintain your fuel system to ensure optimal performance and prevent breakdowns.
Exhaust System
Have you ever wondered how the exhaust system works in gas cars? Well, it’s an essential component responsible for removing harmful exhaust gases produced during the combustion of fuel. The exhaust system has several parts, including the exhaust manifold, catalytic converter, muffler, and tailpipe. The exhaust manifold attaches to the cylinder head and collects exhaust gases from each cylinder.
These gases then exit through the catalytic converter, where they pass through a honeycomb-like structure coated with precious metals that reduce harmful emissions. The muffler is responsible for reducing the noise produced by the exhaust gas, and the tailpipe directs the gases away from the car. If any of these components malfunction, it can cause problems like reduced fuel efficiency and increased emissions.
Therefore, it’s essential to ensure your exhaust system is well-maintained and in good working condition to keep both your car and the environment healthy.
How Electric Cars Work
Electric cars have become increasingly popular in the last few years, but how do they work? Unlike gas cars, electric cars run on batteries that power an electric motor. When you charge the battery, the electric motor converts that stored energy into motion to move the car. The motor has fewer components than a gas engine, making it more efficient and simpler, resulting in less maintenance needed.
Additionally, electric cars have regenerative braking that recovers energy when the car slows down or stops and stores it back in the battery, making it even more efficient. While gas cars emit pollutants, electric cars produce zero emissions and are much better for the environment. As technology advances, electric cars are becoming more affordable and have a longer range, making them a great alternative to gas cars.
So, when it comes to the gas vs. electric car technology debate, it’s clear that electric cars are the future.
Electric Motor
Electric Motor Electric cars are becoming increasingly popular due to their eco-friendliness and economic efficiency. But how does an electric car work? The answer lies in its electric motor. An electric motor converts electrical energy into mechanical energy that powers the wheels of the car.
Unlike internal combustion engines, electric motors have no tailpipe emissions and are incredibly efficient at converting energy. The motor is powered by a battery pack that stores energy from an external power source, such as a charging station or a home outlet. In addition to powering the car, the motor also works to regenerate energy when the car is braking, storing it back in the battery pack for later use.
One of the most significant advantages of electric motors is their simplicity – they have fewer moving parts and require less maintenance than gasoline engines. This leads to fewer breakdowns and lower operating costs for electric car owners. Overall, electric motors have revolutionized the automobile industry, offering a cleaner and more sustainable mode of transportation for the future.
Battery Pack and Charging
When it comes to electric cars, the battery pack is one of the most important components. This is where all the energy is stored for the vehicle to run. Typically, electric cars use lithium-ion batteries, as they are lightweight and can hold a charge for a long time.
After the battery pack is charged, it can be used to power the electric motor that runs the car. But what happens when the battery runs out of power? This is where charging comes in. Electric cars can be charged at home, at public charging stations, or even through regenerative braking.
Regenerative braking is a process whereby the motor acts like a generator, using the kinetic energy of the car to recharge the battery pack as it slows down. Charging times can vary depending on the type of battery and the charging method used, but overall, electric cars offer a convenient and eco-friendly alternative to traditional gasoline vehicles. So, if you’re considering going electric, make sure to factor in charging when making your decision.
Regenerative Braking
Regenerative braking is a technology that electric cars use to capture the energy that is usually wasted during braking. When an electric car is coasting or braking, it uses the motor as an electric generator, converting the energy that is usually lost as heat and friction into electrical energy that can be stored in the car’s battery. This energy can then be used to power the car later on, reducing the need to recharge the battery as often.
It’s a bit like a bicycle with a dynamo that charges a battery while you ride – except in this case, it’s the car itself that generates the electricity! Regenerative braking is one of the key ways that electric cars are able to achieve such impressive ranges on a single charge, and it’s a great example of how clever engineering can turn waste into a valuable resource.
Benefits and Drawbacks
When it comes to driving, there are two major types of cars: gas and electric. Gas cars run on gasoline, while electric cars run on electric motors powered by rechargeable battery packs. Gas cars have been around for over a century and are widely accepted and used, while electric cars are still gaining traction in the automotive industry.
However, the popularity of electric cars is growing rapidly due to their environmental efficiency and cost-effectiveness. Gas cars have higher emissions, require more maintenance, and are more expensive to operate in the long run. On the other hand, electric cars are cheaper to operate, emissions-free, and require minimal maintenance.
The downside is that electric cars have limited range and require a charging infrastructure that is not yet fully developed. Overall, both types of cars have their benefits and drawbacks, and it is crucial to consider each before deciding which one is the best fit for you.
Gas vs Electric Efficiency
When it comes to choosing between gas and electric appliances, there are benefits and drawbacks to both options. In terms of efficiency, electric appliances tend to be more energy-efficient than their gas counterparts. This is because electric appliances convert almost all of the energy they use into heat, while gas appliances lose some energy in the combustion process.
However, gas appliances are often faster and more powerful than electric ones. Additionally, gas can be more cost-effective in certain regions, depending on the availability and cost of electricity and natural gas. Ultimately, the right choice for you depends on your personal preferences and needs.
It’s important to consider factors such as cost, energy efficiency, and overall performance when making your decision. By weighing the benefits and drawbacks of both gas and electric appliances, you can make an informed choice that meets your needs while also being kind to the environment.
Environmental and Cost Impacts
When it comes to renewable energy sources, there are numerous benefits and drawbacks to consider. On the positive side, renewable energy sources have far less impact on the environment when compared to traditional fossil fuels. They emit no harmful pollutants and contribute much less significantly to climate change.
Additionally, renewable energy sources are typically less expensive to operate and maintain relative to other power sources. However, there are also drawbacks to consider. Renewable energy sources are often intermittent, meaning they rely on weather conditions or the time of day, which could limit their reliability and overall effectiveness.
The initial cost of installing renewable energy sources can also be high, hindering adoption rates for smaller businesses and individuals. Despite the potential drawbacks, the benefits of renewable energy sources are undeniable and, as technology and infrastructure continue to advance, it is expected that these drawbacks will become less significant.
Future of Gas and Electric Technologies
The future of gas and electric technologies is rapidly evolving, with improvements being made to both types of vehicles. Gas cars are becoming more fuel-efficient, with hybrid models that run on both gasoline and electric power gaining popularity. Electric cars are not only becoming more affordable but also have longer ranges and faster charging times.
Governments around the world are also incentivizing the purchase of electric vehicles to reduce carbon emissions and combat climate change. As technology continues to advance, we may see a shift towards more eco-friendly options such as hydrogen fuel cell cars. Overall, the future of gas and electric technologies is looking bright, with endless possibilities for innovation and sustainability.
Conclusion
In the world of transportation, there are two main players: gas-powered and electric-powered vehicles. While both offer their own unique benefits, advancements in gas-electric car technology have opened up a whole new realm of possibilities. Gas-electric hybrids combine the best of both worlds, offering fuel-efficient and environmentally friendly options without sacrificing power or performance.
Think of it like a cocktail: the perfect combination of two great things that create a whole new flavor experience. So cheers to the future of gas-electric car technology – a delicious blend of power, efficiency, and sustainability.”
FAQs
How does gas-electric car technology work?
Gas-electric car technology combines the use of a fuel engine and an electric motor. The electric motor helps to power the car at low speeds, and the fuel engine engages at higher speeds. The battery pack is charged via regenerative braking and powers the electric motor.
What are the benefits of gas-electric car technology?
Gas-electric car technology offers several benefits, including better fuel efficiency, reduced emissions, and improved performance. The electric motor helps to reduce the reliance on the fuel engine, which can lead to significant fuel savings.
How does regenerative braking in gas-electric car technology work?
Regenerative braking is a process that involves capturing energy while braking and storing it in the battery pack. The electric motor runs in reverse and acts as a generator to capture the energy that is normally lost during braking. This stored energy can then be used to power the electric motor and reduce the strain on the fuel engine.
How does the size of the battery pack impact the performance of a gas-electric car?
The size of the battery pack can impact the performance of a gas-electric car. A larger battery pack can offer greater range and better acceleration, but it can also increase the overall cost of the vehicle. A smaller battery pack may reduce the range and acceleration but can be more affordable. It’s important to consider the trade-offs when choosing a gas-electric car.