The Electrifying Evolution of Cars: A Deep Dive into the History of Electric Vehicles by John Fuller
Electric cars are increasingly popular, and you may be wondering: where did they come from? The history of electric cars spans almost two centuries and is filled with innovation, competition, and technological progress. From the first crude electric vehicles of the 1800s, to the sleek and efficient models we have today, electric cars have come a long way. In this blog, we’ll take a fascinating journey through time and explore the people, the ideas, and the breakthroughs that have made electric cars what they are today.
Whether you’re an electric vehicle enthusiast or simply interested in the history of technology, sit back and enjoy the ride!
Early Days of Electric Cars
John Fuller, when we talk about the early days of electric cars, we are referring to the 19th and the early 20th centuries. Believe it or not, electric cars were more widespread than gasoline-powered cars at that time. They were not only quiet and convenient but also clean.
However, the development of the gasoline engine by Henry Ford led to the mass production of gas-powered cars, which eventually became more affordable for the general public. This, in turn, reduced the demand for electric cars since they were more expensive to manufacture. Fast forward to the present day, and we see a renewed interest in electric cars due to increased environmental awareness.
Advances in battery technology have made electric cars more efficient, affordable, and practical for everyday use. So, John Fuller, the future of electric cars looks bright, and we can look forward to seeing more of them on our roads.
The Birth of the Electric Car
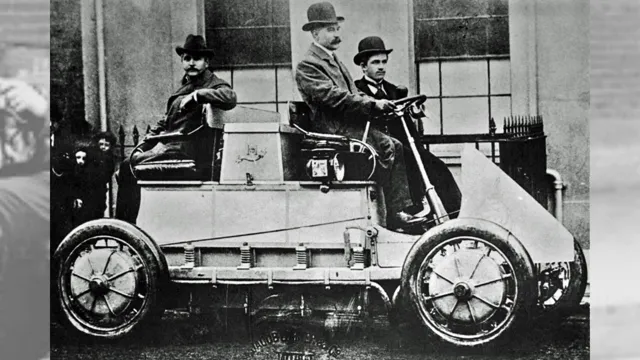
The early days of electric cars, also known as EVs, can be traced back to the late 1800s. It was during this time that inventions like the battery and the electric motor were coming into their own, making it possible for electric vehicles to be built. In fact, the very first electric car was developed in 1832 by Scottish inventor Robert Anderson.
However, it wasn’t until the 1900s that electric cars really gained widespread popularity, thanks to advances in battery technology and the discovery of cheap and abundant oil, which made gasoline cars more affordable. Despite this, electric cars continued to be developed and refined over the years, with notable models such as the EV1 in the 1990s and the Tesla Roadster in the 2000s. Today, with a growing emphasis on sustainability and reducing carbon emissions, the electric car continues to gain traction and evolve, proving that the future of the automobile may very well be electric.

Electric Cars and the First Automobiles
In the early days of automotive history, electric cars were among the first types of automobiles to hit the roads. These early electric vehicles, also known as EVs, are often overlooked in favor of their gasoline-powered counterparts, but their contributions to the development of cars can’t be ignored. One of the first electric cars ever made was built by Thomas Davenport, an American inventor, around the same time as the first gasoline-powered car hit the road.
While electric cars were popular among early car enthusiasts due to their quiet operation and lack of exhaust fumes, the technology simply wasn’t advanced enough to compete with the range and power of gasoline engines. However, with continuous development and advancements in battery technology, electric cars are now seeing a resurgence in popularity as they become a more practical and eco-friendly alternative to gasoline-fueled cars.
The Rise and Fall of Electric Cars
John Fuller, the history of electric cars is a fascinating and tumultuous one. The early days of electric cars saw them as a popular alternative to gasoline-powered vehicles, with companies such as Baker Electric and Detroit Electric producing thousands of vehicles a year. However, the invention of the electric starter by Charles Kettering in 1912 allowed gasoline cars to become much more accessible, leading to a decline in the popularity of electric cars.
Fast forward to the 1990s and 2000s, and electric cars once again began to rise in popularity, with companies such as Tesla leading the charge in creating sleek and innovative electric vehicles. However, the high cost of production and limited range of early electric cars meant that they were still not a practical option for many consumers. It wasn’t until the advent of mass-produced, affordable electric cars such as the Nissan Leaf and Chevrolet Bolt that electric cars finally began to take off.
Today, electric cars have become an increasingly common sight on roads around the world, as consumers have become more concerned about the environmental impact of fossil fuel-powered vehicles. As we move further into the future, it seems likely that electric cars will continue to rise in popularity, with major automakers investing heavily in the development and production of electric vehicles.
The Invention of the Internal Combustion Engine
The internal combustion engine was a monumental invention that revolutionized transportation, but it also brought about the rise and fall of electric cars. Electric cars first made an appearance in the late 1800s and were initially very popular. However, the widespread adoption of the internal combustion engine led to a decline in the popularity of electric cars.
Gasoline was cheap, and the internal combustion engine had a longer range and more power than electric cars at the time. It wasn’t until the 1990s when electric cars made a comeback with improved technology and increasing environmental concerns. Today, electric cars are becoming increasingly popular as more people recognize the benefits of sustainable transportation.
However, the internal combustion engine still dominates the market, and there are many hurdles to overcome before electric cars can fully surpass it. The key to the success of electric cars will be continued innovation and investment in the technology, and a shift towards more sustainable practices in our society.
Advancements in Automobile Technology and the Decline of Electric Cars
The advancements in automobile technology have been nothing short of remarkable in recent years. Cars are becoming faster, smarter, and more efficient than ever before. However, this progress has come at a cost – the decline of electric cars.
Electric vehicles were once hailed as the future of the automobile industry, but they have failed to live up to expectations. There are several reasons for this. Firstly, electric cars have struggled to match the performance and range of traditional gasoline-powered vehicles.
Additionally, the lack of charging infrastructure has made it difficult for drivers to travel long distances without having to stop and recharge. Finally, the price of electric cars has remained high, making them unaffordable for many consumers. Despite these challenges, electric cars continue to have a crucial role in reducing greenhouse gas emissions and combating climate change.
As technology continues to evolve, we may yet see a resurgence in the popularity of electric vehicles.
Electric Cars in the 21st Century
Electric Cars Electric cars have been around for over a century, but gained popularity in the early 2000s due to concerns over climate change and fuel prices. However, their popularity soon dwindled due to a number of factors. One of the main factors was the high cost of batteries, which made electric cars significantly more expensive than their gas-powered counterparts.
Additionally, the limited range of early electric cars made them impractical for long-distance travel. As a result, electric cars were largely relegated to niche markets and were not widely adopted by the general public. However, in recent years, electric cars have begun to make a comeback.
Advances in battery technology have led to longer ranges and lower costs, making electric cars more practical and affordable for everyday use. Furthermore, concerns over climate change and air pollution have prompted governments around the world to incentivize the adoption of electric cars through tax breaks and other measures. As a result, electric cars are now seen as a viable alternative to gas-powered vehicles, and are expected to become increasingly popular in the coming years.
Overall, the rise and fall of electric cars is a story of technological and societal progress. While electric cars may have had their setbacks in the past, they are now poised to become a major force in the 21st century automotive industry, offering a more sustainable and eco-friendly alternative to gas-powered vehicles. So hop on board, because the electric vehicle revolution is just beginning!
The Future of Electric Cars
John Fuller, when looking at the history of electric cars, can trace their roots back to the 19th century. Electric cars were actually the first type of vehicle to be produced and were quite popular until the production of gasoline cars in the early 20th century. Recently, however, electric cars have been making a comeback due to advancements in technology and environmental concerns.
The future of electric cars is looking bright, with more and more car manufacturers investing in their development. Electric cars offer a sustainable, cost-effective mode of transportation that emits zero emissions, making them an ideal solution to combating climate change. As demand for such vehicles rises, we can expect more innovation in the field to cater to the needs of consumers.
With the evolution of electric cars, the world may soon move to a greener future, something that we all can look forward to.
Government Incentives and Regulations
As the world shifts towards sustainable living, the future of electric cars looks bright. Governments around the globe are incentivizing EVs by offering tax exemptions, subsidies, and rebates. For instance, countries like Norway and the Netherlands have implemented policies that waive taxes and provide subsidies to EV buyers.
On the other hand, regions like California, China, and the UK have put in place regulations that encourage automakers to reduce their carbon footprint. As a result, automakers are now investing in electric vehicle technology, driving down costs and increasing availability. The rise of EVs is expected to revolutionize the automotive industry and usher in a new era of green transportation.
With improved battery technology, charging infrastructure, and innovative designs, electric cars will soon overtake traditional gas-powered cars in the market. The shift towards e-mobility shows that the world is committed to combating climate change, and the incentives and regulations in place will only hasten the adoption of EVs.
The Advantages of Going Electric
The future of electric cars is looking very bright indeed, and it’s not just environmentally-conscious drivers who are taking notice. There are a multitude of benefits to going electric, including significant savings on fuel costs and maintenance. Electric cars have fewer moving parts, which means fewer things can go wrong and need to be fixed.
Plus, with so many automakers committing to developing electric vehicles (EVs), the technology and infrastructure supporting them are improving rapidly. The burst in demand for EVs has led to a variety of options for buyers, from economy models to luxury vehicles. With the cost of batteries falling rapidly, and the efficiency of EVs steadily increasing, it’s clear that the advantages of going electric will only continue to grow in the coming years.
Conclusion
So, in brief, the history of electric cars has been a series of stops and starts, with moments of great promise followed by periods of neglect or outright rejection. But now, with increasing concern over climate change and dwindling fossil fuels, electric cars are poised for a resurgence. As with any technology, the key is to learn from the past and keep moving forward, with innovation and determination leading the way.
As the famous inventor Thomas Edison once said, “I have not failed. I’ve just found 10,000 ways that won’t work.” The electric car may have had many false starts, but one thing’s for sure – it’s not going anywhere anytime soon.
FAQs
Who is John Fuller and what is his connection to electric cars?
John Fuller is a historian who has extensively studied the history of electric cars. He has published several books and articles on the topic.
When were electric cars first developed and how did they become popular?
Electric cars were first developed in the 1830s, but they only became popular in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. This was due to the expansion of electricity infrastructure and the invention of the lead-acid battery.
Why did electric cars lose popularity in the mid-20th century?
Electric cars lost popularity in the mid-20th century due to several factors, including the availability of cheap gasoline and improvements in internal combustion engine technology. Electric cars also faced stiff competition from new types of cars, such as hybrids and diesel cars.
How have electric cars evolved over the years?
Electric cars have undergone significant technological advancements over the years, including improvements in battery technology, charging infrastructure, and range. Modern electric cars can travel hundreds of miles on a single charge and can be charged in as little as 30 minutes.