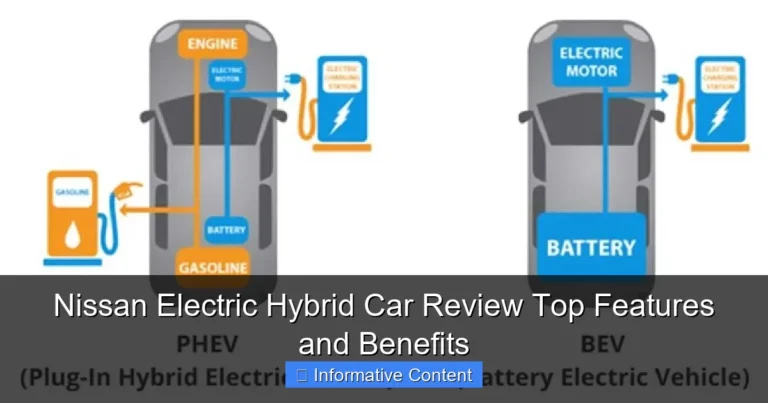
Nissan Leaf Electric Car Mileage How Far Can It Go

Featured image for nissan leaf electric car mileage
Image source: i.ytimg.com
The Nissan Leaf delivers an impressive 149 to 212 miles per charge, depending on the model year and battery size, making it a practical choice for daily commutes and urban driving. With efficient energy use and regenerative braking, the Leaf maximizes every kilowatt-hour for real-world range you can rely on.
Key Takeaways
- Max range: New Nissan Leafs offer up to 212 miles on a single charge.
- Efficiency matters: Real-world mileage depends on driving habits and terrain.
- Regen braking: Use B-mode to recover energy and extend mileage per charge.
- Battery health: Older models may see reduced range due to battery degradation.
- Climate impact: Extreme temperatures can lower mileage by up to 30%.
- Charging speed: Level 2 charging restores 10–25 miles of range per hour.
📑 Table of Contents
- The Electric Revolution: Nissan Leaf Takes the Lead
- Nissan Leaf Models and Their Official Mileage Range
- Factors That Affect Nissan Leaf Mileage in Real-World Driving
- Maximizing Your Nissan Leaf’s Range: Practical Tips and Strategies
- Comparing Nissan Leaf Mileage to Other Electric Cars
- Planning Long Trips: Can the Nissan Leaf Handle Road Trips?
- Conclusion: How Far Can the Nissan Leaf Go?
The Electric Revolution: Nissan Leaf Takes the Lead
The world of electric vehicles (EVs) is rapidly evolving, and at the forefront stands the Nissan Leaf, a pioneer that has redefined what it means to drive green. Since its debut in 2010, the Leaf has become one of the most recognizable and accessible electric cars on the market. With over 500,000 units sold globally, it’s clear that drivers are embracing the benefits of zero-emission driving. But one of the most common questions potential buyers have is: How far can the Nissan Leaf go on a single charge? This blog post dives deep into the Nissan Leaf electric car mileage, exploring real-world range, factors that influence it, and how it stacks up against competitors.
Understanding the range of an electric car isn’t just about numbers on a spec sheet—it’s about peace of mind. Whether you’re commuting to work, taking a weekend road trip, or navigating city traffic, knowing your vehicle’s capabilities is essential. The Nissan Leaf offers different battery options and model years with varying ranges, making it crucial to understand the nuances. From the early 151-mile Leaf to the latest 212-mile Leaf Plus, the journey has been one of continuous improvement. Let’s explore how far the Nissan Leaf can truly go and what you need to know before hitting the road.
Nissan Leaf Models and Their Official Mileage Range
The Nissan Leaf lineup has evolved significantly since its introduction, with multiple battery sizes and trims offering different ranges. The key to understanding the Nissan Leaf electric car mileage lies in distinguishing between the standard Leaf and the Leaf Plus (also known as Leaf e+). These models differ primarily in battery capacity, which directly impacts their range.
Standard Nissan Leaf (40 kWh Battery)
The standard Nissan Leaf comes equipped with a 40 kWh lithium-ion battery. According to the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), this model delivers an estimated range of 149 miles on a full charge. However, real-world testing and driver reports often show slightly lower numbers, averaging between 120–140 miles under mixed driving conditions. This range is ideal for daily commuters, urban drivers, and those with access to charging at home or work.
- Best for: City dwellers, short commutes, and budget-conscious buyers.
- Example: A driver with a 30-mile round-trip commute can go 4–5 days without needing to recharge.
- Tip: Use regenerative braking (e-Pedal) to extend range during stop-and-go traffic.
Nissan Leaf Plus (62 kWh Battery)
The Leaf Plus, introduced in 2019, features a larger 62 kWh battery and delivers a significantly improved range. The EPA rates the Leaf Plus at 212 miles per charge—a 42% increase over the standard model. In real-world conditions, drivers typically achieve 180–200 miles, depending on driving habits and environmental factors. This makes the Leaf Plus a viable option for longer road trips and suburban drivers with higher daily mileage.
- Best for: Families, long-distance commuters, and those seeking more flexibility.
- Example: A 100-mile round trip can be completed with 50% battery remaining, allowing for flexibility in charging.
- Tip: Precondition the cabin while charging to save battery power for driving.
Historical Range Improvements (2011–2023)
The evolution of the Nissan Leaf’s range tells a story of technological progress. The first-generation Leaf (2011–2017) started with a 24 kWh battery offering just 73–84 miles. By 2018, the second-generation model introduced the 40 kWh battery, nearly doubling the range. The 2019 Leaf Plus marked a leap forward, bringing the Leaf into competition with newer EVs like the Chevrolet Bolt and Tesla Model 3 Standard Range.
This progression highlights Nissan’s commitment to improving battery density, efficiency, and thermal management. While the Leaf still doesn’t match the 300+ mile ranges of premium EVs, its Nissan Leaf electric car mileage is now competitive in the affordable EV segment.
Factors That Affect Nissan Leaf Mileage in Real-World Driving
While EPA estimates provide a baseline, the actual range you get from your Nissan Leaf depends on a variety of real-world factors. Understanding these variables can help you maximize efficiency and plan your trips with confidence.
1. Driving Speed and Behavior
Speed has a dramatic impact on electric car range. The Nissan Leaf is most efficient at speeds between 30–50 mph. At highway speeds (65+ mph), aerodynamic drag increases significantly, reducing range by up to 25%. Aggressive acceleration and high-speed cruising drain the battery faster.
- Tip: Use cruise control and smooth acceleration to maintain efficiency.
- Example: A 20-mile highway trip at 70 mph may use the same energy as a 35-mile city drive at 35 mph.
2. Weather and Temperature
Extreme temperatures—both hot and cold—reduce battery performance. In cold weather (below 32°F/0°C), lithium-ion batteries become less efficient, and cabin heating draws power. Studies show that the Leaf can lose 30–40% of its range in sub-freezing conditions. Conversely, hot weather (above 90°F/32°C) can also reduce range due to battery cooling needs.
- Tip: Preheat or cool the cabin while plugged in to avoid using battery power.
- Example: A Leaf Plus with a 212-mile range may only achieve 130 miles in winter if the heater is used heavily.
3. Terrain and Elevation
Hilly or mountainous terrain increases energy consumption. Climbing steep grades requires more power, while descending offers some regenerative braking recovery—but not enough to fully offset the climb.
- Tip: Plan routes using apps like A Better Routeplanner (ABRP) to estimate elevation impact.
- Example: A 50-mile drive with 1,000 feet of elevation gain may consume 15% more energy than a flat route.
4. Use of Climate Control and Accessories
Heating, air conditioning, and seat warmers draw power from the battery. The Leaf’s HVAC system is efficient but still impacts range. Using seat heaters instead of the cabin heater can save up to 5% in cold weather.
- Tip: Use Eco mode and set the cabin temperature to 68–72°F for optimal balance.
5. Tire Pressure and Vehicle Load
Underinflated tires increase rolling resistance, reducing efficiency. Similarly, carrying heavy cargo or passengers adds weight, requiring more energy. Keeping tires at the recommended pressure (36–38 PSI) can improve range by 3–5%.
- Tip: Check tire pressure monthly and remove unnecessary items from the trunk.
Maximizing Your Nissan Leaf’s Range: Practical Tips and Strategies
Getting the most out of your Nissan Leaf electric car mileage isn’t just about the car’s specs—it’s about how you drive and maintain it. With a few smart habits, you can extend your range and reduce charging frequency.
Use Regenerative Braking (e-Pedal Mode)
The Nissan Leaf features a one-pedal driving mode called e-Pedal. When activated, it increases regenerative braking, allowing the car to slow down and recapture energy by simply lifting off the accelerator. This can add 5–10 miles of range per charge in city driving.
- How to use: Press the e-Pedal button on the center console and drive using only the accelerator.
- Tip: Practice in a safe area to get used to the braking feel.
Precondition the Cabin While Charging
Heating or cooling the cabin while the Leaf is plugged in draws power from the grid, not the battery. This preserves your driving range, especially in winter.
- How to set: Use the NissanConnect app or in-car timer to schedule preconditioning 15–30 minutes before departure.
- Example: A 20-minute preheat at 60°F saves 10% of battery compared to heating while driving.
Adopt Efficient Driving Habits
Smooth acceleration and coasting can significantly improve efficiency. Avoid rapid starts and hard braking. Use the Leaf’s Eco mode, which softens throttle response and optimizes energy use.
- Tip: Watch the energy consumption display (kWh/100mi) and aim for lower numbers.
- Target: 280–300 watt-hours per mile (Wh/mi) for optimal efficiency.
Optimize Charging Strategy
Charging to 100% isn’t always necessary or beneficial. For daily use, charging to 80% preserves battery health and reduces charging time. Save full charges for long trips.
- Tip: Use the NissanConnect app to set a charging limit (e.g., 80%) for overnight charging.
- Bonus: Level 2 chargers (240V) are more efficient than Level 1 (120V), adding 20–30 miles of range per hour.
Maintain the Battery Health
Over time, lithium-ion batteries degrade. To slow this process, avoid deep discharges (below 20%) and extreme temperatures. Park in the shade or a garage when possible.
- Tip: Use the Leaf’s battery health display to monitor long-term performance.
- Fact: Most Leafs retain 80–85% of their original range after 8 years.
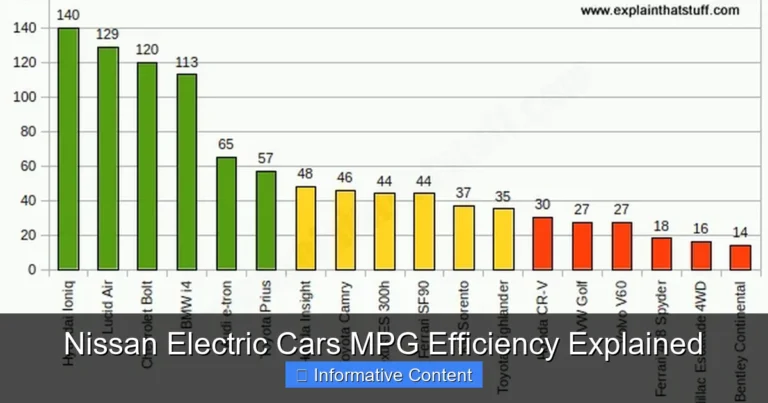
Comparing Nissan Leaf Mileage to Other Electric Cars
How does the Nissan Leaf electric car mileage stack up against the competition? Let’s compare the Leaf and Leaf Plus to key rivals in the affordable EV segment.
| Vehicle | Battery Size (kWh) | EPA Range (Miles) | Real-World Range (Miles) | Price (MSRP) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nissan Leaf S (40 kWh) | 40 | 149 | 120–140 | $28,040 |
| Nissan Leaf Plus (62 kWh) | 62 | 212 | 180–200 | $36,040 |
| Chevrolet Bolt EV | 65 | 259 | 220–240 | $26,500 |
| Hyundai Kona Electric | 64 | 258 | 210–230 | $34,000 |
| Kia Niro EV | 64 | 253 | 210–225 | $39,550 |
| Tesla Model 3 Standard Range | 50 | 272 | 230–250 | $38,990 |
The Nissan Leaf holds its own in the value segment. While it doesn’t match the 250+ mile ranges of the Bolt, Kona, or Model 3, the Leaf Plus offers a compelling balance of price, range, and features. For drivers with daily commutes under 100 miles, the standard Leaf is highly practical. The Leaf’s strengths include:
- Lower starting price than most competitors (after federal tax credit).
- Proven reliability with over a decade of real-world use.
- Strong resale value in the used EV market.
- Ease of use with intuitive controls and a user-friendly infotainment system.
Where the Leaf Falls Short
The Leaf’s CHAdeMO fast-charging standard is a limitation. Unlike CCS (used by most rivals), CHAdeMO is less common on public fast-charging networks. This can slow down road trips compared to CCS-equipped EVs. Additionally, the Leaf’s interior materials and tech feel dated compared to newer models.
Planning Long Trips: Can the Nissan Leaf Handle Road Trips?
One of the biggest concerns for EV owners is long-distance travel. Can the Nissan Leaf—especially the Leaf Plus—handle a cross-country journey? The answer is yes, with planning.
Charging Infrastructure and Route Planning
With the Leaf Plus’s 212-mile range, most intercity trips are feasible. Use apps like PlugShare, A Better Routeplanner (ABRP), or ChargePoint to map charging stops. The Leaf supports Level 3 DC fast charging (CHAdeMO), which can add 80% of range in 45–60 minutes.
- Tip: Plan charging stops every 150–180 miles to stay within safe range.
- Example: A 400-mile trip from Los Angeles to Las Vegas can be done with two 45-minute charges.
Fast Charging Capabilities
The Leaf Plus can charge at up to 100 kW on compatible CHAdeMO stations. In ideal conditions, it can go from 10% to 80% in about 45 minutes. However, charging speeds drop as the battery fills and in cold weather.
- Tip: Start charging at 20–30% and stop at 80% for the fastest speeds.
Real-World Road Trip Example
Imagine a 300-mile trip from San Francisco to Lake Tahoe. The route includes steep climbs and cold temperatures. A Leaf Plus driver might:
- Precondition the cabin while charging at home.
- Drive efficiently, using cruise control and e-Pedal.
- Stop at a fast charger in Sacramento (120 miles in), adding 60 miles of range.
- Arrive in Tahoe with 30% battery remaining, then charge overnight at a hotel.
This trip is entirely feasible and highlights how Nissan Leaf electric car mileage can support real-world adventures with smart planning.
Tips for Stress-Free EV Road Trips
- Download offline maps of charging stations in case of poor signal.
- Carry a portable Level 2 charger for backup.
- Use hotel charging to top up overnight.
- Check weather forecasts and adjust plans if cold fronts are expected.
Conclusion: How Far Can the Nissan Leaf Go?
The Nissan Leaf electric car mileage has come a long way since its debut. Today, the standard Leaf offers a reliable 120–140 miles of real-world range, while the Leaf Plus delivers 180–200 miles—enough for most daily needs and many weekend getaways. While it may not match the 300-mile ranges of premium EVs, the Leaf shines in affordability, reliability, and ease of use.
Understanding the factors that affect range—speed, temperature, terrain, and driving habits—empowers you to get the most out of every charge. With smart strategies like preconditioning, regenerative braking, and efficient driving, you can extend your range and reduce charging stops. And for those considering long trips, the Leaf Plus, paired with careful planning, is more than capable of handling the journey.
Whether you’re a first-time EV buyer or upgrading from an older model, the Nissan Leaf remains a compelling choice. Its evolution reflects the broader progress in electric mobility: longer ranges, better batteries, and growing charging infrastructure. So, how far can the Nissan Leaf go? The answer is: as far as you need it to—with a little knowledge, a lot of confidence, and the freedom of electric driving.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the real-world mileage of the Nissan Leaf electric car?
The Nissan Leaf offers a real-world range of 150–226 miles per charge, depending on the model year and battery size (40 kWh vs. 62 kWh). Factors like driving habits, terrain, and climate can slightly reduce this mileage.
How does cold weather affect Nissan Leaf electric car mileage?
Cold weather can reduce the Nissan Leaf’s mileage by up to 30–40% due to increased energy use for heating and battery inefficiency in low temperatures. Preconditioning while plugged in helps mitigate this loss.
Can the Nissan Leaf go 300 miles on a single charge?
No, even the longest-range Nissan Leaf (with the 62 kWh battery) has an EPA-estimated 226 miles. For 300+ miles, consider EVs like the Tesla Model 3 or Hyundai Ioniq 6.
Does highway driving reduce Nissan Leaf mileage significantly?
Yes, highway driving at high speeds reduces Nissan Leaf mileage by 15–25% compared to city driving due to aerodynamic drag. The Leaf’s efficiency drops above 65 mph.
How does battery degradation impact Nissan Leaf electric car mileage over time?
After 5–7 years, Nissan Leaf batteries typically retain 70–80% capacity, reducing mileage by 20–30%. Regular use of fast charging accelerates degradation slightly.
Is the Nissan Leaf mileage enough for daily commuting?
For most drivers, the Leaf’s 150–226 mile range is sufficient for daily commutes (average U.S. commute is 40 miles). Overnight charging easily covers weekly driving needs.