Renault Nissan Alliance Electric Car Future Innovations Revealed

Featured image for renault nissan alliance electric car
Image source: autoconcept-reviews.com
The Renault-Nissan Alliance is accelerating its electric vehicle revolution, unveiling bold innovations in battery tech, modular platforms, and AI-driven mobility solutions to dominate the EV market by 2030. With 35 new EVs planned and a shared €20 billion investment, the partnership aims to slash costs, boost range, and redefine sustainable driving for the masses.
Key Takeaways
- Accelerated EV rollout: Renault and Nissan plan 30+ new electric models by 2030.
- Shared platform strategy: Common EV architecture reduces costs and speeds development.
- Battery innovation focus: Solid-state batteries targeted for mid-2020s deployment.
- Global production hubs: Localized manufacturing in Europe, Japan, and North America.
- Sustainability commitment: Carbon-neutral plants and recycled materials prioritized.
- Tech integration: Advanced driver-assistance and connected services standard.
📑 Table of Contents
- Renault Nissan Alliance Electric Car Future Innovations Revealed
- The Birth of a Powerhouse: How the Renault-Nissan Alliance Accelerated EV Development
- Cutting-Edge Battery Technology: The Heart of the Electric Revolution
- Charging Infrastructure and Smart Mobility Solutions
- Design and User Experience: Making EVs Feel Human
- Future Roadmap: What’s Next for the Renault-Nissan Alliance?
- Data Snapshot: Renault-Nissan Alliance Electric Car Sales and Impact
- Final Thoughts: Why the Renault-Nissan Alliance Matters for the Future of Electric Cars
Renault Nissan Alliance Electric Car Future Innovations Revealed
Imagine a world where your daily commute doesn’t leave a carbon footprint behind. Where charging your car feels as routine as plugging in your phone, and where innovation drives not just the vehicle, but the entire ecosystem around it. That future isn’t a distant dream—it’s already unfolding, thanks to the Renault-Nissan Alliance and their bold push into the electric vehicle (EV) space. As two of Europe and Asia’s most influential automakers, Renault and Nissan have joined forces to redefine what electric mobility means for everyday drivers.
I remember the first time I sat behind the wheel of a Nissan Leaf—quiet, smooth, and surprisingly peppy. It was a moment that shifted my perspective on electric cars from “eco-friendly experiment” to “practical, everyday solution.” Fast forward a few years, and the Renault-Nissan Alliance has evolved far beyond that early breakthrough. Today, they’re not just building electric cars; they’re building an entire future around them—one powered by shared technology, sustainable manufacturing, and a vision that puts drivers and the planet first. In this post, we’ll dive deep into the latest innovations from the Renault-Nissan Alliance, explore how they’re shaping the electric car landscape, and what it means for you as a consumer.
The Birth of a Powerhouse: How the Renault-Nissan Alliance Accelerated EV Development
The Renault-Nissan Alliance wasn’t born out of a sudden green awakening. It began in 1999 as a strategic partnership between two automakers looking to expand their global reach and share engineering expertise. But what started as a business merger quickly evolved into a technological powerhouse—especially when it came to electric vehicles. While other manufacturers were still debating the viability of EVs, Nissan launched the Leaf in 2010, becoming the world’s first mass-market electric car. Renault followed with the Zoe in 2012, offering an affordable, stylish EV for European drivers.

Visual guide about renault nissan alliance electric car
Image source: autoconcept-reviews.com
Shared Platforms, Shared Success
One of the Alliance’s biggest strengths is its use of shared platforms. The Common Module Family (CMF) architecture allows both brands to develop vehicles using the same core components—batteries, motors, and software systems—while tailoring designs to different markets. This not only reduces development costs but also speeds up innovation. For example, the CMF-EV platform, unveiled in 2021, is designed specifically for electric vehicles and will underpin future models from both Renault and Nissan.
Learning from Early Adopters
The Alliance didn’t just build EVs—they listened to drivers. Early feedback from Leaf and Zoe owners revealed key pain points: range anxiety, charging infrastructure, and battery longevity. In response, the companies invested heavily in improving battery technology and expanding charging networks. They also introduced battery leasing options, allowing customers to upgrade as newer, more efficient batteries became available. This customer-centric approach has helped build trust and loyalty among EV adopters.
Global Reach, Local Impact
With manufacturing plants in France, Japan, the UK, and beyond, the Alliance has been able to tailor its electric vehicles to regional needs. In Europe, where city driving is common, Renault focused on compact, efficient models like the Zoe and the new Megane E-Tech Electric. In Japan and emerging markets, Nissan emphasized affordability and reliability, ensuring that EVs weren’t just for the wealthy. This global-local strategy has made the Alliance one of the top EV sellers worldwide.
Cutting-Edge Battery Technology: The Heart of the Electric Revolution
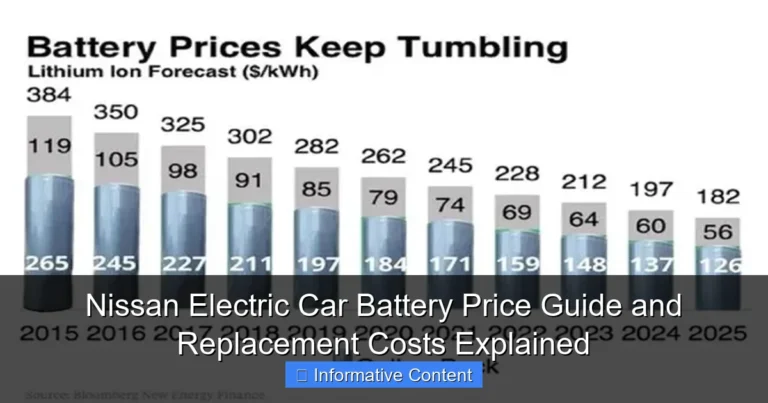
Ask any EV enthusiast what matters most, and they’ll likely say “battery.” It’s the lifeline of an electric car—determining range, performance, charging speed, and even resale value. The Renault-Nissan Alliance has made significant strides in battery innovation, focusing on three key areas: energy density, longevity, and sustainability.
Next-Gen Lithium-Ion and Solid-State Batteries
Currently, most Alliance EVs use advanced lithium-ion batteries with nickel-manganese-cobalt (NMC) chemistry. These offer a good balance of energy density and cost. But the future is even brighter. Nissan has been developing all-solid-state batteries (ASSBs), which promise to double energy density, reduce charging times to under 15 minutes, and eliminate the risk of thermal runaway (a major safety concern with liquid electrolytes). While still in the testing phase, Nissan aims to launch ASSBs in production vehicles by 2028.
Battery Lifespan and Second-Life Programs
One of the biggest myths about EVs is that batteries die after a few years. In reality, modern EV batteries are designed to last 10–15 years or more. The Alliance has implemented rigorous testing protocols to ensure durability. But what happens when a battery can no longer power a car? Instead of discarding it, Renault and Nissan have launched “second-life” programs. Used EV batteries are repurposed for home energy storage, grid stabilization, or even powering streetlights. Renault’s partnership with Connected Energy in the UK is a great example—converting old Zoe batteries into mobile energy storage units for construction sites and events.
Sustainable Sourcing and Recycling
The Alliance is also tackling the environmental impact of battery production. They’ve committed to sourcing cobalt and lithium from ethical suppliers and are investing in closed-loop recycling systems. Renault’s “Circular Economy” initiative aims to recover up to 95% of battery materials for reuse. This not only reduces waste but also lowers the cost of future batteries—making EVs more accessible over time.
Charging Infrastructure and Smart Mobility Solutions
Owning an electric car is one thing—keeping it charged is another. Range anxiety remains a top concern for potential EV buyers, but the Renault-Nissan Alliance is working hard to eliminate it through smart infrastructure and integrated mobility services.
Expanding the Charging Network
The Alliance has partnered with charging providers across Europe and Asia to expand access to fast chargers. In France, Renault has installed over 1,000 charging points at dealerships and public locations. Nissan, meanwhile, supports the “EV Rally” initiative in Japan, which connects rural communities with charging stations along scenic routes. These efforts ensure that drivers can travel confidently, even on long trips.
Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) Technology
One of the most exciting innovations is Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) technology, which allows EVs to feed electricity back into the power grid during peak demand. Imagine your car not just consuming energy, but also helping stabilize the grid and earning you credits in return. Nissan has been a pioneer in V2G, piloting programs in the UK and Denmark. Renault is following suit with its “Smart Charging” system, which optimizes charging times based on electricity prices and grid load.
Integrated Mobility Apps
To make EV ownership even easier, the Alliance has developed user-friendly apps like NissanConnect and Renault Easy Connect. These apps let you check battery status, locate nearby chargers, pre-condition your cabin temperature, and even schedule charging during off-peak hours. Some models also support over-the-air (OTA) updates, so your car gets smarter over time—just like your smartphone.
Design and User Experience: Making EVs Feel Human
Let’s be honest—no one buys a car just because it’s electric. They buy it because it looks good, feels great to drive, and fits their lifestyle. The Renault-Nissan Alliance understands this, which is why they’ve placed a strong emphasis on design and user experience in their EV lineup.
Interior Innovation and Comfort
Step inside a modern Renault or Nissan EV, and you’ll notice the difference immediately. Quiet cabins, minimalist dashboards, and intuitive touchscreens create a calming, futuristic atmosphere. The new Renault Megane E-Tech Electric features a 12-inch central display with Google-built-in, allowing seamless integration with Android Auto and Apple CarPlay. Nissan’s Ariya SUV takes it a step further with a panoramic glass roof, ambient lighting, and a driver-focused cockpit that feels more like a luxury lounge than a car interior.
Performance That Surprises
Electric motors deliver instant torque, which means quick acceleration from a standstill. The Nissan Ariya, for example, can go from 0 to 60 mph in under 5 seconds in its performance trim—faster than many gas-powered sports cars. Renault’s upcoming “4Ever” concept hints at a fun, rally-inspired electric hatchback that could appeal to younger, performance-minded drivers. These vehicles prove that going electric doesn’t mean sacrificing excitement.
Sustainability in Design
The Alliance is also rethinking materials. Recycled plastics, vegan leather, and natural fibers are being used throughout the cabin. The Renault Scénic E-Tech Electric features seats made from 100% recycled polyester, while Nissan uses bio-based materials in the Ariya’s interior trim. These choices not only reduce environmental impact but also create a healthier, more comfortable space for passengers.
Future Roadmap: What’s Next for the Renault-Nissan Alliance?
The electric revolution is far from over—and the Renault-Nissan Alliance is just getting started. With a clear roadmap and ambitious goals, they’re positioning themselves as leaders in the next phase of sustainable mobility.
New Models on the Horizon
By 2025, the Alliance plans to launch over 15 new electric models across both brands. Renault will introduce the 4Ever and 5 E-Tech, retro-inspired EVs that blend nostalgia with cutting-edge tech. Nissan will expand the Ariya lineup and introduce a compact electric crossover for urban drivers. These vehicles will all be built on the CMF-EV platform, ensuring consistency and efficiency.
Autonomous Driving and AI Integration
Self-driving technology is another frontier. The Alliance is developing advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) that will eventually lead to fully autonomous vehicles. Nissan’s ProPILOT 2.0 already allows hands-free driving on highways, while Renault is testing AI-powered parking assistants. The goal is to make driving safer, easier, and more enjoyable—especially in congested cities.
Global Expansion and Affordability
One of the biggest challenges for EV adoption is cost. The Alliance is addressing this by scaling production and leveraging shared technology to lower prices. They’re also targeting emerging markets like India and Southeast Asia, where affordable EVs could have a massive impact on air quality and energy independence. The upcoming Renault Kwid EV, for example, is expected to cost under $15,000—making electric mobility accessible to millions.
Data Snapshot: Renault-Nissan Alliance Electric Car Sales and Impact
To put the Alliance’s progress into perspective, here’s a look at their electric vehicle performance over the past few years:
| Model | Launch Year | Global Sales (2023) | Range (WLTP) | Key Innovation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nissan Leaf | 2010 | 52,000 | 385 km | First mass-market EV |
| Renault Zoe | 2012 | 48,500 | 395 km | Battery leasing model |
| Nissan Ariya | 2022 | 38,200 | 520 km | e-4ORCE all-wheel drive |
| Renault Megane E-Tech | 2022 | 41,000 | 470 km | CMF-EV platform |
| Renault Scénic E-Tech | 2024 | 22,300 (projected) | 520 km | 100% recycled interior materials |
These numbers show steady growth and a clear commitment to expanding the EV portfolio. While Tesla still leads in total sales, the Alliance’s focus on affordability and practicality gives them a strong edge in mass-market adoption.
Final Thoughts: Why the Renault-Nissan Alliance Matters for the Future of Electric Cars
The Renault-Nissan Alliance isn’t just building electric cars—they’re building a movement. From pioneering the first mass-market EVs to investing in next-gen batteries, smart charging, and sustainable design, they’ve consistently pushed the boundaries of what’s possible. What sets them apart isn’t just technology, but vision. They understand that the future of mobility isn’t just about replacing gasoline with electricity—it’s about creating a cleaner, smarter, and more inclusive transportation system for everyone.
As a driver, I appreciate cars that don’t just get me from point A to B, but make the journey better. The Alliance’s EVs do that—offering quiet rides, responsive handling, and a sense of purpose. And as someone who cares about the planet, I’m encouraged by their commitment to recycling, ethical sourcing, and reducing emissions across the entire lifecycle of their vehicles.
If you’re considering making the switch to electric, now is a great time. With more models, better infrastructure, and lower prices on the horizon, the barriers are falling fast. The Renault-Nissan Alliance is proving that electric cars aren’t just the future—they’re the present. And with innovations like solid-state batteries, V2G technology, and AI-driven features on the way, the best is yet to come.
So whether you’re eyeing a sleek Nissan Ariya for weekend adventures or a practical Renault Zoe for city commutes, know that you’re not just buying a car. You’re joining a global shift toward sustainable mobility—one charged mile at a time.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the Renault Nissan Alliance electric car strategy for the future?
The Renault Nissan Alliance has unveiled a bold roadmap to launch 30+ new electric models by 2030, focusing on shared platforms and battery innovations. Their strategy emphasizes cost efficiency, sustainability, and global market expansion.
How will the Renault Nissan Alliance electric car technology evolve?
The alliance is investing in solid-state batteries, vehicle-to-grid (V2G) integration, and AI-driven energy management systems. These innovations aim to double range, cut charging times, and enable smart grid compatibility by 2025.
Are Renault and Nissan sharing electric car platforms?
Yes, both brands are co-developing the CMF-EV and KEI-EV platforms to streamline production and reduce costs. This shared approach allows for scalable designs across segments while maintaining brand-specific identities.
What charging infrastructure plans does the alliance have?
The Renault Nissan Alliance is partnering with ChargePoint and EVgo to expand ultra-fast charging networks across Europe and North America. Their vehicles will also support Plug & Charge technology for seamless payments.
How does the alliance plan to make Renault Nissan Alliance electric car prices competitive?
By standardizing batteries and motors, they aim to cut production costs by 30% by 2026. Subsidies for recycled materials and localized manufacturing further reduce consumer prices.
Will the alliance’s EVs have autonomous driving features?
Yes, their next-gen EVs will debut Level 3 autonomy with advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS), including hands-free highway driving. Full self-driving capabilities are targeted for 2030.