The Comprehensive Guide to Electric Car Charging Stations
Electric car charging stations are pivotal components in the electric vehicle (EV) ecosystem, providing the necessary infrastructure for recharging EV batteries. These stations vary in charging speed and type, accommodating different EV models and user needs. Innovations in technology and increasing global distribution are making these stations more accessible and efficient, supporting the widespread adoption of electric vehicles.
Electric car charging stations are rapidly becoming an integral part of the urban landscape, signifying a significant shift towards sustainable transportation. As the adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) accelerates globally, the need for accessible and efficient charging infrastructure becomes increasingly crucial. These stations not only facilitate the recharging of EV batteries but also serve as a testament to technological advancement and environmental commitment. The varied types of charging stations, ranging from slow to rapid charging, cater to diverse user needs, making EVs more practical for everyday use.
The development and expansion of electric car charging stations are driven by technological innovations, economic factors, and governmental policies. As the backbone of the electric vehicle movement, these stations play a vital role in reducing carbon emissions and fostering a greener future. The emergence of smart, connected charging networks, along with the integration of renewable energy sources, marks a new era in the automotive and energy sectors. This comprehensive guide delves into the multifaceted world of electric car charging stations, exploring their technical, economic, and environmental aspects, and envisioning their future in the evolving landscape of transportation.
1. Overview of Electric Car Charging Stations
Importance in the EV Ecosystem
Electric car charging stations are the lifeline of the electric vehicle (EV) ecosystem. They provide the essential service of recharging EV batteries, a process that replaces the refueling of traditional gasoline vehicles. The availability and efficiency of these stations directly impact the usability and appeal of EVs to the general public. As the EV market grows, the development of an extensive and reliable charging infrastructure becomes crucial for sustaining this growth. These stations serve not just as mere utility points but as symbols of a paradigm shift towards sustainable and innovative transportation solutions.
Types and Varieties of Charging Stations
There are primarily three types of electric car charging stations – Level 1, Level 2, and DC Fast Charging (Level 3). Level 1 chargers are the most basic, offering a slow charging process, typically used at home. Level 2 chargers are faster and are commonly found in public and commercial settings. DC Fast Chargers are the quickest, providing substantial charge in a short period, ideal for long-distance travel. Each type caters to different needs, from everyday commuting to rapid, on-the-go recharging.
Global Distribution and Availability
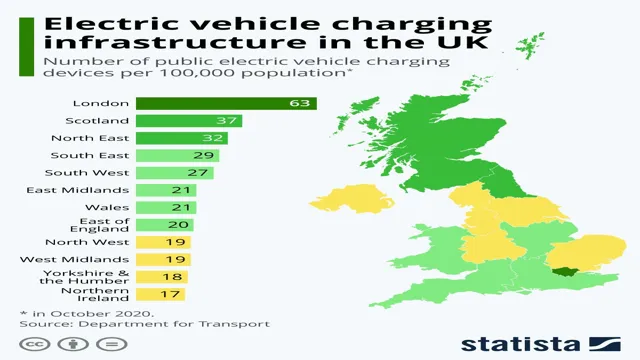
The distribution of electric car charging stations varies globally, with higher concentrations in urban and developed regions. Europe, North America, and parts of Asia, especially China, are leading in the installation of EV charging infrastructure. Governments and private companies are increasingly investing in expanding the network of charging stations to cover more areas, including remote and rural locations. This expansion is crucial for alleviating ‘range anxiety’ – a common concern among potential EV buyers about running out of charge away from a charging point.
2. Technical Aspects of Electric Car Charging
Understanding Charging Levels and Speeds
Electric car charging stations are categorized into different levels based on their charging speed. Level 1 charging, typically done using a standard household outlet, offers a charging speed of about 2-5 miles of range per hour. Level 2 charging, more common in public and commercial areas, can provide about 12-80 miles of range per hour. DC Fast Charging, the fastest available, can charge an EV battery to 80% in as little as 30 minutes, depending on the vehicle and charger specifications. Understanding these levels is crucial for EV users to manage their charging schedules and travel plans effectively.
Connector Types and Compatibility
The EV charging industry uses several types of connectors to accommodate different vehicle models and charging standards. The most common types include the J1772 connector for Level 1 and 2 charging in the U.S., the CCS (Combined Charging System) for DC Fast Charging, and the CHAdeMO connector, primarily used by Japanese vehicles. Tesla vehicles use a proprietary connector but offer adapters for other types. This variety requires EV users to be aware of the compatibility of their vehicles with available charging stations, especially when traveling.
Innovations in Charging Technology
Technological advancements are continually improving the efficiency and convenience of EV charging. Innovations include ultra-fast charging technologies, which aim to reduce charging times significantly, and smart charging systems that can optimize charging schedules based on grid demand and energy prices. Wireless charging technology, still in the developmental stage, promises a future where EVs can be charged without physical cable connections, offering greater convenience for EV users.
3. Setting Up Electric Car Charging Stations
Location Considerations
When establishing electric car charging stations, location is a critical factor. Ideal locations are easily accessible and visible to drivers, such as near highways, shopping centers, and public parking areas. Urban areas generally require more stations due to higher population density and EV usage. However, installing charging stations along major travel corridors and in rural areas is essential to support long-distance travel and broaden EV adoption.
Installation Requirements
Installing an EV charging station involves several technical and logistical considerations. For Level 2 and DC Fast Charging stations, professional installation is required to handle the high-voltage equipment. This includes site preparation, ensuring electrical capacity, and installing the necessary hardware. Compliance with local and national electrical codes and standards is crucial for safety and functionality.
Permits and Legal Requirements
Setting up charging stations often requires navigating a variety of permits and legal requirements. These can include building permits, electrical permits, and adherence to ADA (Americans with Disabilities Act) guidelines. In many regions, there are specific regulations governing the installation and operation of EV charging stations. It’s important for installers and site owners to be aware of and comply with these regulations to ensure a smooth setup process and legal operation.
4. Economic Aspects of Charging Stations
Investment and Operating Costs
The investment required for electric car charging stations varies based on the type of charger and the complexity of the installation. Level 1 chargers are the least expensive, while Level 2 and DC Fast Chargers require a higher upfront investment. Operating costs include electricity, maintenance, and network fees if the station is part of a charging network. Understanding these costs is crucial for businesses and municipalities considering investing in EV infrastructure.
Revenue Models for Charging Stations
There are various revenue models for electric car charging stations. Some operate on a pay-per-use basis, where users pay per charging session or per kWh of electricity. Subscription models offer unlimited charging for a monthly fee. Additionally, charging stations can drive indirect revenue by attracting customers to businesses or enhancing property value.
Economic Benefits and ROI
The economic benefits of installing electric car charging stations extend beyond direct revenue. They can increase property values and attract eco-conscious customers to businesses. For municipalities, they support local economic development and can qualify for government grants and incentives. The return on investment (ROI) for charging stations can be favorable, especially as EV adoption continues to grow and demand for charging increases.
5. Charging Station Design and Aesthetics
Design Innovations for User Convenience
Modern electric car charging stations are designed with user convenience in mind. This includes easy-to-use interfaces, clear instructions, and seamless payment methods. Some stations are equipped with features like retractable cables, adjustable charging speeds, and weatherproof materials for user comfort and ease of use.
Integrating Charging Stations in Urban Landscapes
The integration of charging stations into urban landscapes requires careful planning. They should complement the existing infrastructure and urban design, and not obstruct pedestrian or vehicle traffic. Creative designs and thoughtful placement can make charging stations an aesthetically pleasing part of the urban fabric.
Aesthetic Considerations
Aesthetics play a significant role in the acceptance and integration of electric car charging stations. Sleek, modern designs can enhance the appeal of these stations, making them more than just functional infrastructure. The use of sustainable materials and innovative design can also reflect the eco-friendly nature of EVs, further promoting their adoption.
6. Networks and Connectivity of Charging Stations
Building Connected Charging Networks
The development of connected electric car charging networks is a significant advancement in the EV infrastructure. These networks allow for the integration of multiple charging stations across different locations, providing EV drivers with extensive coverage and convenience. Connectivity also enables real-time data sharing about station availability, pricing, and charging speed, improving the user experience. Major players in the industry are collaborating to build expansive networks, ensuring interoperability between different charging systems and providers.
The Role of IoT and Smart Technology
Internet of Things (IoT) and smart technology are revolutionizing electric car charging stations. Smart chargers can communicate with the power grid to optimize charging times, based on energy demand and pricing. This helps in balancing the grid load and promotes the use of renewable energy sources when available. Additionally, smart chargers provide remote monitoring and management capabilities, enhancing operational efficiency and user convenience.
Enhancing User Experience Through Connectivity
Connectivity enhances the user experience by offering features like mobile app integration, where users can locate chargers, check availability, and even reserve charging slots. Advanced systems provide updates on charging progress and notifications when charging is complete. Such features not only add convenience but also help in efficient energy management and reducing waiting times at busy charging stations.
7. Charging Station Accessibility and Inclusivity
Addressing Accessibility Issues
Accessibility is a crucial aspect of electric car charging station design and placement. Stations must be accessible to all users, including those with disabilities. This involves considering factors like the height of charging equipment, clear signage, and ease of physical access. Inclusivity in design ensures that the transition to electric vehicles is equitable and does not leave any group of society behind.
Inclusive Design Principles
Inclusive design principles focus on creating charging stations that are user-friendly for a diverse range of drivers. This includes multilingual interfaces, clear and simple instructions, and user interfaces that are intuitive for people of all ages and abilities. By incorporating these principles, charging stations become more welcoming and usable for the entire community.
Overcoming Geographic and Economic Barriers
To promote widespread EV adoption, it’s essential to overcome geographic and economic barriers in charging station accessibility. This means installing charging infrastructure not only in affluent urban areas but also in underserved and rural regions. Financial incentives, public-private partnerships, and community-driven initiatives play a vital role in making EV charging stations accessible and affordable for all segments of the population.
8. Sustainability and Green Initiatives
Leveraging Renewable Energy Sources
Electric car charging stations are increasingly incorporating renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, to reduce their carbon footprint. This integration not only makes EV charging more sustainable but also aligns with global efforts to combat climate change. The use of green energy sources also adds to the appeal of EVs as truly eco-friendly transportation options.
Reducing Carbon Footprint
The shift to electric vehicles, supported by sustainable charging infrastructure, plays a significant role in reducing the overall carbon footprint of transportation. By using electricity from renewable sources, EV charging stations can offer a truly zero-emission solution. This is crucial in urban areas, where reducing greenhouse gas emissions is a high priority.
Sustainable Practices in Charging Station Operations
Sustainable practices in the operation and maintenance of electric car charging stations include using energy-efficient components, minimizing waste, and employing eco-friendly materials. Companies are also exploring recycling programs for retired EV batteries and using them for energy storage at charging stations. Such practices not only enhance the environmental benefits of EVs but also set an example for sustainability in other industries.
9. Government Policies and Incentives
Policy Framework for EV Infrastructure
Government policies play a crucial role in shaping the development and expansion of electric car charging infrastructure. Many countries have implemented policies that support the deployment of EV charging stations through funding, tax incentives, and regulatory support. These policies are designed to accelerate the transition to electric vehicles by making charging infrastructure more accessible and affordable. For instance, governments may mandate the installation of charging stations in new residential and commercial developments or provide subsidies for the installation of public charging stations.
Incentives for Charging Station Installation
Various incentives are offered by governments to encourage the installation of electric car charging stations. These can include tax breaks, grants, rebates, and low-interest loans. In some regions, utilities also offer incentives for EV charging to manage grid demand effectively. These incentives are critical for reducing the upfront costs associated with setting up charging stations, making it a more viable option for businesses and municipalities.
Global Policy Trends
Around the world, there is a growing trend of governments actively promoting electric vehicle infrastructure. In Europe, for example, there are ambitious targets for the number of EV charging stations, backed by substantial investment. Similarly, in the United States, federal and state governments are introducing various measures to support the EV market. These trends reflect a global commitment to reducing carbon emissions and transitioning to sustainable transportation solutions.
10. Emerging Trends in Electric Car Charging
Advances in Battery Technology
Battery technology is advancing rapidly, influencing the development of electric car charging stations. Improvements in battery capacity and efficiency directly impact the charging process, allowing for faster charging times and longer driving ranges. Emerging technologies, such as solid-state batteries, promise to revolutionize EV charging by offering higher energy density and faster charging capabilities.
Autonomous and AI-based Charging Solutions
The integration of autonomous and AI-based technologies in EV charging is an emerging trend. Autonomous charging robots, for instance, can navigate parking areas to charge vehicles without human intervention. AI algorithms optimize charging schedules based on user patterns and grid demands, enhancing the efficiency of charging station networks. These innovations are set to make EV charging more seamless and integrated into daily life.
Future Projections and Innovations
The future of electric car charging stations is poised for significant innovation. This includes the development of ultra-fast charging technologies that could charge EVs in minutes, integration of charging stations with smart city infrastructure, and the use of blockchain for secure and transparent payment systems. As EV adoption grows, these innovations will be critical in ensuring that the charging infrastructure keeps pace with demand and continues to evolve.
11. Cost Analysis of Electric Car Charging Stations
Initial Setup Costs
The initial setup costs of electric car charging stations vary significantly based on the type of charger and the complexities of installation.
- Level 1 Charging Stations: These are the most basic and cost-effective to set up, often using existing standard electrical outlets. The main costs here are the charging unit and minimal installation expenses.
- Level 2 Charging Stations: These require a more significant investment. Costs include the purchase of the charging unit, electrical upgrades if needed, installation labor, and potentially the cost of obtaining permits. On average, the setup for a Level 2 station can range from a few thousand dollars to over ten thousand dollars per unit.
- DC Fast Chargers (Level 3): The most expensive to install, these chargers can cost anywhere from $30,000 to over $100,000 per unit, including the charger, installation, and necessary electrical infrastructure upgrades. They are typically used in commercial or public settings due to their high power output and rapid charging capability.
Ongoing Operational Costs
Once installed, electric car charging stations incur various operational costs.
- Electricity Costs: The primary recurring expense is the cost of electricity used to charge the vehicles. This cost varies based on local electricity rates and the charger’s utilization rate.
- Maintenance and Repairs: Regular maintenance is required to keep charging stations operational. This includes costs for parts, labor, and routine inspections.
- Network Fees: If the charging station is part of a larger network, there might be associated network fees. These fees can cover software updates, customer service, and access to network-specific features like user analytics or remote troubleshooting.
- Insurance and Liability: Some level of insurance is often necessary to cover potential damages or liabilities associated with operating charging stations.
Cost-Saving Strategies
To manage and reduce the costs associated with electric car charging stations, several strategies can be employed.
- Government Incentives and Grants: Many governments offer incentives, rebates, or grants to offset the initial setup costs. Researching and taking advantage of these financial aids can significantly reduce upfront expenses.
- Partnerships: Forming partnerships with other businesses or entities can help distribute the costs. For instance, a retail store might partner with a charging station provider to offer charging services, sharing the costs and benefits.
- Dynamic Pricing Models: Implementing dynamic pricing for charging services can optimize revenue. Prices can be varied based on demand, time of day, or power usage, helping to balance the grid load and maximize profit.
- Energy Management Systems: Integrating smart energy management systems can reduce operational costs by optimizing charging times based on energy tariffs and grid demand, leading to lower electricity costs.
- Solar Power Integration: For long-term savings, integrating renewable energy sources like solar panels can reduce reliance on grid power, leading to significant reductions in operational costs over time.
The cost analysis of electric car charging stations underscores the importance of strategic planning and optimization to ensure financial viability and sustainability. As the market for EVs continues to grow, the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of the charging infrastructure will play a crucial role in supporting this transition.
12. Real-world Examples and Success Stories
Urban Case Studies:
- Amsterdam’s “Lamppost Charging”: Amsterdam transformed existing lampposts into charging points, providing over 2,800 charging locations in the city center. This efficient solution increased EV adoption by 20% within a year, but challenges remain in managing peak demand and integrating charging into historic districts.
- Seoul’s “Charging Hubs”: Strategically placed hubs offer various charging speeds (from slow to ultra-fast) and amenities like cafes and shops. This model caters to diverse needs and fosters community, attracting over 100,000 users monthly. However, concerns arise about hub saturation and equitable access across all neighborhoods.
- London’s “Workplace Charging Initiatives”: Programs incentivize businesses to offer charging, leading to over 17,000 workplace charging points installed. This boosts employee EV adoption and reduces reliance on public charging. However, challenges include limited parking space and ensuring fair access for all employees.
Rural Case Studies:
- California’s “Charge Across California”: This network of fast chargers along major highways addresses range anxiety concerns. With 200 stations operational, travel and tourism have increased in rural areas. However, concerns remain about long-term funding and equitable access beyond tourist routes.
- Norway’s “Rural Charging Infrastructure Grants”: The program has funded over 1,500 charging stations in rural communities, bridging the urban-rural gap. Local ownership fosters community engagement and economic benefits. However, challenges include maintaining sufficient funding and attracting private investment in remote areas.
- Scotland’s “EV Community Charging Fund”: Communities own and operate charging points, empowering them to tailor solutions to local needs. This model has led to over 200 community-owned charging points. However, challenges include initial investment costs and ensuring long-term maintenance and operation.
Innovative Business Models
- Subscription-based Models: Services like Tesla Supercharger Network and Electrify America offer unlimited charging for a monthly fee, attracting frequent users and generating predictable revenue. However, high subscription costs limit accessibility for casual users.
- Public-Private Partnerships: Collaborations like Ionity in Europe and EVgo in the US leverage public funding and private expertise to expand infrastructure. This model accelerates development but requires careful contract design and risk sharing.
- Retail and Hospitality Integration: Supermarkets like Carrefour and hotels like Hilton offer charging as an additional service. This attracts customers and increases dwell time, but requires upfront investment and revenue sharing agreements.
- Peer-to-Peer Charging Platforms: Platforms like GetMyCharge and Neighbor Charging connect EV owners with spare chargers. This promotes community-driven solutions and affordability, but concerns exist about user verification and ensuring quality and safety.
Global Best Practices
- Standardization and Interoperability: Universal charging standards like CCS and CHAdeMO ensure seamless charging across networks and countries. This boosts user convenience and market growth, but requires ongoing collaboration between manufacturers and governments.
- Smart Grid Integration: Integrating charging stations with smart grids optimizes energy use, balances demand, and promotes renewable energy sources. This requires advanced technology and collaboration between grid operators and charging providers.
- Data-driven Decision Making: Data collected from charging stations informs planning, pricing strategies, and infrastructure development. This requires robust data collection, analysis capabilities, and transparent data sharing practices.
- Regulatory Frameworks: Effective regulations encourage investment, set safety standards, and promote fair competition. This requires balancing innovation with consumer protection and environmental sustainability.
Pioneering Cities and Countries
Several cities and countries are leading the way in the deployment of electric car charging stations. For example, cities like Oslo and Amsterdam have extensive networks of EV chargers, supported by strong government policies and public enthusiasm for electric vehicles. Similarly, countries like Norway and China have made significant strides in EV infrastructure, setting examples for others to follow.
Successful Business Models in Charging Infrastructure
Innovative business models are emerging in the electric car charging station industry. Companies are exploring partnerships with retail outlets, where charging stations attract customers who can shop while their vehicle charges. Other successful models include offering charging as a value-added service in hotels, workplaces, and apartment complexes. These models not only provide convenience to EV owners but also create new revenue streams for businesses.
Lessons Learned and Best Practices
The growth of the EV charging infrastructure provides valuable lessons and best practices. Key among these is the importance of strategic placement of charging stations to maximize accessibility and usage. Collaborations between governments, businesses, and communities are also crucial for successful deployment. Furthermore, incorporating user feedback into the design and operation of charging stations ensures they meet the needs of EV drivers.
Conclusion
The development of electric car charging stations is a dynamic and evolving field, integral to the global shift towards sustainable transportation. With advancements in technology, supportive government policies, and innovative business models, the infrastructure for EV charging is expanding rapidly. As we look to the future, the continued growth and evolution of this infrastructure will be key to supporting the widespread adoption of electric vehicles and achieving environmental sustainability goals.
FAQ
- How do different charging station levels affect charging time? Level 1 chargers offer slow charging, typically overnight for a full charge. Level 2 chargers are faster, suitable for daily use, providing a full charge in a few hours. DC Fast Chargers are the quickest, charging an EV to about 80% in 30 minutes.
- What are the environmental benefits of using electric car charging stations? Electric car charging stations, especially those powered by renewable energy, help reduce greenhouse gas emissions by supporting zero-emission electric vehicles. They are crucial in the transition to a more sustainable transportation system.
- How can businesses benefit from installing charging stations? Businesses can attract eco-conscious customers, increase foot traffic, and potentially generate additional revenue through charging services. Charging stations also enhance the company’s green image and commitment to sustainability.
- What are the latest technological advancements in EV charging? Recent advancements include ultra-fast charging technologies, wireless charging, smart charging systems integrated with the grid, and the use of AI for optimizing charging schedules and operations.
- How is government policy shaping the future of electric car charging stations? Government policies are critical in driving the growth of EV charging infrastructure through incentives, subsidies, and regulations. They help lower the barriers to entry, encouraging investment in charging technology and expanding the network of available charging options.