Uncovering the Fascinating History of Electric Cars: From Early Inventions to Modern Innovations
Electric cars have been around for over a century, but it’s only in recent years that they’ve gained mainstream attention. It’s hard to imagine a world without electric vehicles, but the road to their success hasn’t been easy. The journey of electric cars is a long and surprising one, filled with detours, setbacks, and unexpected twists.
Despite being around for more than 100 years, electric cars were mostly seen as a novelty and didn’t gain much popularity until the early 21st century. The modern electric car movement started in the late 1990s, with the launch of the Toyota Prius, the first mass-market hybrid car. This was followed by the Tesla Roadster in 2008, which revolutionized the electric vehicle market.
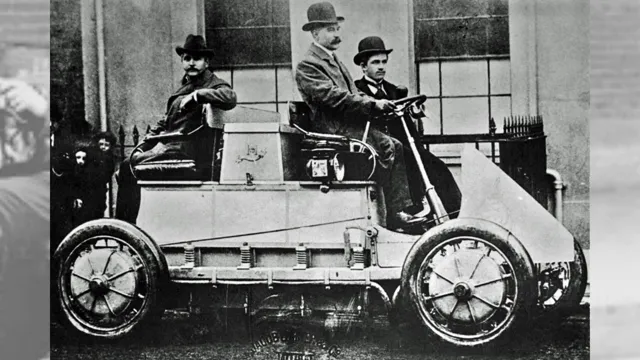
However, the electric car’s story begins much earlier. The first electric car was invented in the early 1800s, but it wasn’t until the late 19th century that they started to become more common. At the turn of the 20th century, electric cars were a popular choice among wealthy American families, with electric cars outselling gasoline cars until the 1920s.
The decline of electric cars was due to several factors, including the development of the internal combustion engine, increased oil production, and improvements in road infrastructure. Electric vehicles were no longer seen as a viable option, and they were replaced by gasoline-powered cars. However, in recent years, electric cars have made a comeback.
With concerns about climate change and the rising price of gas, electric cars have become a popular choice for eco-conscious consumers. The introduction of new technology, such as longer-lasting batteries and fast charging stations, has made electric cars more practical and accessible. In conclusion, the story of electric cars is a long and winding one.
From the early 1800s to the present day, electric cars have seen their fair share of ups and downs. However, with the current popularity of electric vehicles and the push towards sustainability, it’s clear that electric cars are here to stay.
Early History of Electric Cars
The surprisingly long history of electric cars dates all the way back to the 1830s. Yes, you read that right! In fact, electric cars were actually more popular than gasoline cars in the early 1900s. However, when Henry Ford introduced the affordable assembly line for gasoline cars, electric cars became scarce.
It wasn’t until the 1960s and 1970s that electric vehicles made a comeback due to concerns over air pollution and gas prices. Even then, it wasn’t until the 1990s and early 2000s that electric cars gained popularity among consumers. Today, with concerns over the environment and rising gas prices, electric vehicles are becoming more and more popular.
It’s fascinating to see how the history of electric cars has come full circle, from being the preferred mode of transportation to being replaced by gasoline cars, and now gaining popularity once again.
Mid-19th Century Electric Cars
During the mid-19th century, electric cars were already making waves in the automotive industry. Despite facing challenges due to the limitations in battery technology, electric cars were seen as a viable alternative to gasoline-powered vehicles. One of the early pioneers of electric cars was Thomas Davenport, who actually built the first electric car in 183
However, it was not until the 1870s when the first commercial electric cars became available to the public. These electric cars were favored by urban dwellers who preferred a quiet and comfortable ride. They were also seen as environmentally friendly, as they produced no emissions and were powered by renewable energy.
Despite the advancements made in the electric car industry, it wasn’t until the 20th century that gasoline-powered cars became the dominant force. However, the popularity of electric cars continued to grow, leading to the creation of some of the most modern and efficient electric cars on the market today.

Early 20th Century: Electric Cars vs. Gasoline Cars
The early history of electric cars is a fascinating one that dates back to the late 19th century. At the time, electric cars were actually more popular than gasoline cars, especially in urban areas where they were considered cleaner and quieter. In fact, electric cars were even preferred by some of the wealthiest Americans, including Thomas Edison and Henry Ford.
However, the tide began to turn in the early 20th century when gasoline-powered cars became increasingly more powerful and efficient. Gasoline cars could now travel farther distances and at faster speeds, making them more practical for long-distance travel. Additionally, advancements in gasoline engine technology made them more affordable for the average consumer.
Over time, gasoline cars became the dominant vehicle on American roads, and electric cars were largely forgotten until the late 20th century when concerns about air pollution and climate change led to a renewed interest in electric vehicles. It’s amazing to think about how different our transportation landscape might look today if electric cars had remained the norm back in the early 20th century.
The Resurgence of Electric Cars
The resurgence of electric cars is a hot topic of conversation, but did you know that the history of electric vehicles dates back to the early 19th century? Although gasoline-powered vehicles quickly gained popularity, electric cars had their own place in history with a variety of technological advancements and unique features, including quiet motors, easy maneuverability, and lack of emissions. However, it wasn’t until recent years that electric cars truly began to make a comeback, with many people championing the eco-friendly benefits and impressive performance capabilities of modern electric vehicles. Thanks to advancements in battery technology, range anxiety is becoming a thing of the past and more and more consumers are making the switch to electric cars.
It’s fascinating to see how the surprisingly long history of electric cars is now coming full circle, with a bright and exciting future ahead.
1970s-90s: Electric Vehicle Experimentation
The 1970s marked a renewed interest in electric vehicles, with the oil crisis of the 1970s propelling the push for alternative modes of transportation. This led to a surge in experimentation with various types of electric-powered cars, from small neighborhood EVs to larger highway-capable models. Unfortunately, these early electric cars were hampered by a multitude of challenges, including limited range, high costs, and lack of infrastructure for charging and maintenance.
Despite these setbacks, engineers and automakers remained committed to improving electric car technology. In the 1990s, advancements in battery technology and government incentives led to the development of increasingly efficient and practical electric vehicles. This paved the way for the resurgence of electric cars we see today, with modern EVs boasting longer ranges, faster charging times, and more affordable prices.
With more and more consumers recognizing the benefits of electric vehicles, including lower emissions and reduced dependence on non-renewable resources, the future of the automotive industry looks increasingly electric.
Early 2000s: Toyota and Electric Cars
In the early 2000s, Toyota was one of the car manufacturers leading the charge in the resurgence of electric cars. After releasing its first electric vehicle in Japan in 1997, the Prius hybrid was introduced worldwide, and it quickly became a symbol of the shift towards sustainable driving. Toyota’s investment in green technology paid off, as the company saw a significant increase in consumer demand for electric and hybrid vehicles.
In response, Toyota continued to develop its lineup of green cars, including the all-electric RAV4 and the hydrogen fuel cell-powered Mirai. Despite early setbacks, including the discontinuation of some of its electric models due to low sales, Toyota’s commitment to environmentally-friendly transportation has only grown stronger over the years.
Tesla and the Electric Revolution
Tesla is leading the charge in the resurgence of electric cars, and for a good reason. The world is finally waking up to the impact of climate change, and consumers are demanding more eco-friendly alternatives to gas-guzzling cars. Tesla’s sleek designs, cutting-edge technology, and impressive range have helped make electric cars more accessible and appealing to the masses.
But Tesla’s impact goes beyond just making electric cars more popular. Elon Musk’s company is also driving innovation in battery technology, charging infrastructure, and autonomous driving, which could revolutionize the way we think about transportation. As more and more people switch to electric cars, we can expect to see a significant reduction in greenhouse gas emissions and a cleaner, healthier planet.
It’s an exciting time for the electric revolution, and Tesla is at the forefront of it all.
Electric Cars Today and Beyond
The history of electric cars is longer than many people think. The first electric car was built in the 1830s, and by the early 1900s, electric cars actually outnumbered gasoline-powered vehicles. However, with the discovery of large oil reserves and advancements in gasoline engines, electric cars fell out of favor.
It wasn’t until the 1990s that electric cars started to come back into mainstream attention, with Toyota and Honda releasing their first electric vehicles. In recent years, the popularity of electric cars has skyrocketed due to concerns over climate change and advancements in battery technology, making them a viable option for everyday use. As we move towards a more sustainable future, electric cars are poised to play a significant role in transforming the automotive industry.
Current State of Electric Cars
Electric Cars Today and Beyond The current state of electric cars is one of exciting innovation and growth. With recent advancements in battery technology and increased investment from automakers, electric cars are becoming more accessible and practical for everyday use. Today, electric cars offer drivers a convenient and eco-friendly alternative to traditional gas-powered vehicles.
They boast impressive range, acceleration, and efficiency while producing zero emissions. But the future of electric cars goes beyond just the present. The possibilities for electric vehicles are endless, from fully automated self-driving cars to solar-powered charging stations.
The automotive industry is moving towards a greener and more sustainable future, and electric cars are at the forefront of this revolution. As consumers seek environmentally responsible options and governments implement stricter emissions regulations, the electric car market is set to continue its rapid expansion. With every passing day, electric cars are becoming more advanced, more economical, and more attractive to consumers worldwide.
Future Trends in Electric Cars and Sustainable Transport
Electric Cars The future of electric cars is looking bright, with many advancements in technology making them more efficient and affordable than ever before. From increased range and faster charging times to sleek designs and cutting-edge features, electric cars are set to change the face of sustainable transport as we know it. But the benefits of electric cars go beyond just reducing carbon emissions; they also offer savings on fuel costs and provide a smoother, quieter driving experience.
The rise of electric car sharing programs and the integration of renewable energy sources into the charging infrastructure are further indications of the direction that sustainable transport is headed. As more and more people become environmentally conscious and seek alternative modes of transportation, electric cars are poised to become a mainstream mode of transport in the coming years. With all these advancements and benefits, it’s no wonder that electric cars are taking the world by storm, paving the way for a cleaner, greener future.
Final Thoughts on Electric Cars
The surprisingly long history of electric cars goes back more than a century. In fact, the first electric vehicle was built in the late 1800s, but it wasn’t until the early 1900s that electric cars became more mainstream. However, with the rise of gasoline-powered cars, electric cars became less popular and almost disappeared altogether.
It wasn’t until recent years that electric cars became a viable alternative to gasoline-powered vehicles. Advances in technology have made electric cars more practical, efficient, and affordable. Today, electric cars are becoming more popular as people become more aware of the benefits of reducing carbon emissions and saving money on gasoline.
With more options now available, including hybrid and plug-in hybrid models, there are more ways than ever to go green while still enjoying the benefits of owning a car.
Conclusion
In the end, the history of electric cars is not just a story about technology and innovation, it’s a tale of human ingenuity, environmental awareness, and a desire for sustainable transportation. From the clunky early models to the sleek and modern designs of today, electric cars have come a long way. And yet, despite the numerous setbacks and challenges faced by the industry over the years, electric vehicles still remain an important part of the global push towards cleaner, greener energy solutions.
So, if you’re ever wondering why the world is buzzing about electric cars lately, remember that they’ve actually been around for quite some time – and they’re here to stay!”
FAQs
When were the first electric cars invented?
The first electric cars were invented in the 1830s.
Why did electric cars lose popularity in the early 20th century?
Electric cars lost popularity due to the mass production of gasoline-powered vehicles, which were cheaper and had longer driving ranges.
What prompted the recent resurgence of electric cars?
Environmental concerns, government regulations, and advancements in battery technology have all contributed to the recent resurgence of electric cars.
How does the cost of owning an electric car compare to a gasoline-powered car?
The initial cost of purchasing an electric car is typically higher than a gasoline-powered car, but the cost of ownership over time can be lower due to lower fuel and maintenance costs.