The Electrifying Evolution: A Fascinating Timeline of the History of the Electric Car
Welcome to the Electric Car Timeline, where we’ll take a look at the past, present, and future of electric vehicles. In the past few years, the electric car industry has been gaining traction and innovation has been accelerating rapidly. From the early explorations of electric vehicle technology in the late 19th century to the present-day breakthroughs, it has been a long and sometimes bumpy ride.
But what has been the driving force behind the development of electric cars, and what does the future hold? If you’re considering purchasing an electric car, or are just curious about their evolution, this is the place for you. We’ll delve into the history of electric cars, explore the technological advancements that have brought us to our current state, and take a look at what we can expect from the future of electric vehicles. Electric cars are now more accessible, driving longer distances, and charging faster than ever before, and with the world pushing for more sustainable transportation, the future of electric cars looks bright.
In this timeline, we’ll explore how electric cars have come to be one of the most interesting and competitive markets in the automobile industry. Join us in the journey through the electric car timeline, and let’s see where the road takes us.
Early Beginnings
The timeline of the history of the electric car goes back to the early 1800s when the first electric vehicle was invented by Scottish inventor Robert Anderson. However, it wasn’t until the late 1800s that the first practical electric vehicle was developed. In 1888, German engineer Andreas Flocken created a prototype electric car, and in 1891, William Morrison from Iowa built the first successful electric vehicle.
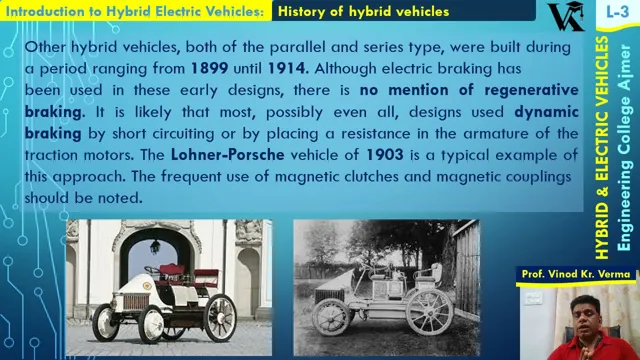
Electric cars were popular in the early 1900s, with manufacturers such as Detroit Electric and Baker Electric producing thousands of units. However, the invention of the gasoline-powered engine and the development of highways led to the decline of electric cars, and by the 1920s, they were no longer in widespread use. Nonetheless, efforts to develop electric cars continued, with major advances made in recent years.
With improvements in battery technology, electric cars have become a viable alternative to traditional gasoline-powered vehicles, and their popularity is expected to continue to grow in the future.
1800s-1900s
In the 1800s and 1900s, the first forms of technology were beginning to emerge, laying the foundation for the technological revolution that would come later in the century. These early beginnings included the invention of the telegraph and the telephone, which made it possible to communicate over long distances in real-time. In addition, the creation of the light bulb and electric power transmission made it possible for people to have electricity in their homes and businesses, and paved the way for the development of many other electrical devices.
Along with these technological advancements, there were also major social and economic changes taking place during this time. For example, the industrial revolution was in full swing, with many new factories being built and more people moving to cities to work in them. This led to new challenges such as the need for better transportation and infrastructure, and the need for regulations to protect workers.
Overall, the early beginnings of the 1800s and 1900s were a time of great change and progress, setting the stage for the world we know today.

Initial Inventions
During the early beginnings of invention, humans have shown great interest in creating tools and gadgets that would make their lives easier. From the discovery of fire to the invention of the wheel and writing system, these early inventions have paved the way for more complex and advanced innovations in the future. These inventions were products of human curiosity and the need to survive in a constantly changing environment.
As civilizations developed, so did their inventions. For example, the ancient Egyptians developed sophisticated irrigation systems to make farming more efficient, while the Chinese invented paper and the compass, which revolutionized communication and navigation. The early inventions of our ancestors may seem primitive by modern standards, but they were the foundation upon which today’s technology was built.
The Rise Of Electric Cars
For over a century, the electric car has been an enigma in the automotive industry. The timeline of the history of the electric car dates back to the late 1800s when inventors started experimenting with electric motors powered by batteries. The first electric car was built in 1837, and by the early 1900s, electric vehicles were common on the streets of major cities, mainly because of their silent, smooth riding and low-maintenance features.
However, the invention of the gasoline-powered engine in the early 20th century took over and dominated the automobile market, leading to the decline of electric cars. It wasn’t until the oil crisis of the 1970s that alternative energy vehicles made a comeback, and in 1996, GM released the EV1, the first electric car made by a major automaker. Today, electric cars have become more mainstream, with companies like Tesla, Nissan, and General Motors investing heavily in research and development to make electric cars more accessible, affordable, and practical.
The timeline of the history of the electric car has come full circle, and electric cars seem to be the future of the automotive industry.
1970s-1990s
In the 1970s-1990s, electric cars began to rise in popularity due to concerns over rising oil prices and environmental issues. The first electric cars were introduced in the early 1970s, although they were limited in range and had high costs. Despite this, the energy crisis of the 1970s caused interest in electric cars to increase as consumers looked for alternatives to traditional gasoline-powered vehicles.
As technology improved, so did the efficiency and range of electric cars, making them a more viable option for consumers. However, despite the advancements made in electric car technology, they still faced a number of challenges, including limited infrastructure for charging and the high cost of batteries. These challenges, coupled with the relatively low gasoline prices of the 1990s, caused electric cars to lose popularity once again.
Nonetheless, the rise of electric cars in the 1970s-1990s marked a significant milestone in the development of alternative energy vehicles, setting the stage for even more advanced electric cars in the future.
The Electric Car Revolution
Electric cars are becoming increasingly popular as people become more environmentally conscious. The rise of electric cars started slowly, with a few niche models being offered by major automakers. However, the market for electric vehicles has exploded in recent years, with nearly all major car companies now offering at least one electric model.
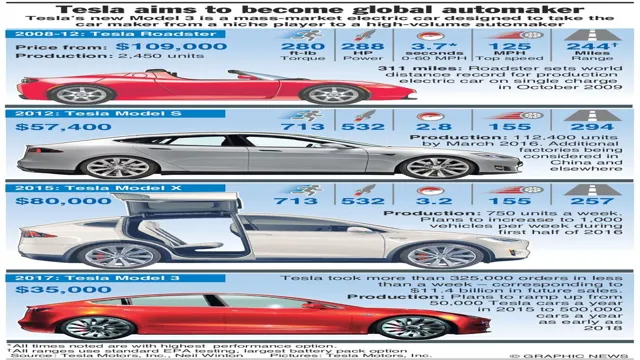
The Tesla Model S was one of the first cars to spark widespread interest in electric cars, but now there are several other options available. The main benefit of electric cars is their lack of emissions, making them a great option for anyone who cares about the environment and wants to reduce their carbon footprint. While there are still some challenges to overcome, such as their limited driving range and the lack of charging infrastructure, electric cars are quickly catching up to gasoline cars in terms of convenience and practicality.
With more and more people making the switch to electric, it’s clear that the electric car revolution is here to stay.
Tesla’s Contributions
Tesla has undoubtedly been a game-changer in the automobile industry, particularly in the rise of electric cars. With their cutting-edge technology and innovative design, Tesla has set a new standard for what an electric vehicle can be. Aside from offering a sustainable mode of transportation, Tesla has also been making contributions towards changing the way energy is generated and consumed.
With the introduction of their Powerwall energy storage system, Tesla has enabled homeowners to harness the power of renewable energy, making it a viable option for those looking to minimize their carbon footprint. As we continue to experience the effects of climate change, Tesla’s contributions towards a greener future are more critical than ever. By driving electric vehicles and utilizing renewable energy solutions, we can all play our part in creating a brighter future for ourselves and generations to come.
Current State Of Electric Cars
The history of electric cars dates back to the 1800s, where they first gained popularity. With the advancement in technology and the urge to battle climate change, electric cars have become more popular in recent years. Tesla’s innovative electric cars have set the stage for electric cars.
They have made electric cars more accessible, with more automakers following suit. As of today, more than 2 million electric vehicles are running worldwide. The current range of electric cars is around 100-150 miles, while some high-end models like the Tesla Models can go over 500 miles in a single charge.
Governments around the world are offering incentives to promote the use of electric cars, such as subsidies for purchasing and installing electric car chargers in homes, businesses and public spaces. The future of electric cars seems bright, with many automakers aiming to electrify their entire line-ups by the end of the decade. As technology advances, it is only a matter of time for electric cars to take over the automobile market.
Global Demand
The current state of electric cars is one of high demand on a global scale. As countries strive to reduce their carbon footprint and embrace renewable energy, electric cars have emerged as a popular alternative to traditional gasoline vehicles. In fact, the International Energy Agency predicts that by 2030, there will be 125 million electric vehicles on the road.
This surge in demand has resulted in an increase in production and availability of electric cars from major car manufacturers. While electric cars still have a higher upfront cost than traditional cars, the long-term cost savings in fuel and maintenance, as well as the environmental benefits, have made them an attractive option for many consumers. As the demand for electric cars continues to grow, we can expect to see more innovations and advancements in this technology, making it an even more viable alternative to fossil fuel-powered vehicles.
Battery Technology Advances
Battery technology advancements have revolutionized the realm of electric cars. The current state of electric vehicles is characterized by improved battery performance, increased range, and reduced charging times. Modern electric cars can travel over 400 miles on a single charge, and ultra-fast charging stations can recharge the batteries up to 80% in just 30 minutes.
That’s a significant improvement from the early electric cars that had a range of only 100 miles and took hours to charge. With the development of new battery technologies like solid-state batteries, electric cars will become even more feasible. While electric cars are still more expensive than gas-powered vehicles, the cost is decreasing as battery technology improves, making them more accessible to the mass market.
Additionally, electric cars are more environmentally friendly, produce less noise pollution, and offer a smooth and quiet ride compared to their gas-powered counterparts. The future of electric cars looks promising, and with continuous advancements in battery technology, we can expect to see more affordable and efficient electric vehicles in the coming years.
Future Of Electric Cars
The history of the electric car dates back to the 1830s when British inventor Thomas Davenport developed a small electric motor. In the late 1800s, electric cars started to pop up in urban areas due to their lack of pollution and noise. However, they were quickly overshadowed by the internal combustion engine, which had a much longer range.
Fast forward to the 21st century, and electric cars are making a comeback as more people become concerned about the environment and the cost of fuel. In 2010, the Nissan Leaf became the first mass-produced electric car, and since then, many companies have followed suit with their own electric models. The future of electric cars is looking bright, with technology advancing rapidly in areas such as battery life and charging infrastructure.
It’s expected that by 2035, almost 50% of new cars sold worldwide will be electric. As we move towards a more sustainable future, the timeline of the history of the electric car will continue to evolve, and we’ll see more and more people making the switch to electric vehicles.
Conclusion
In the timeline of the history of the electric car, we can see the rise, fall, and rise again of this eco-friendly mode of transportation. From the early experimental electric vehicles of the 1800s to the mainstream success of Tesla and other modern electric cars, it’s clear that the electric car is here to stay. So, whether you’re a die-hard EV enthusiast or just looking for a more sustainable way to get around, hop on board the electric ride and join the electrifying revolution!”
FAQs
When was the first electric car invented?
The first electric car was invented in the 1830s.
Who invented the first electric car?
The first electric car was developed by Scottish inventor Robert Anderson.
When did electric cars start becoming popular?
Electric cars gained popularity in the early 1900s, but were later surpassed by gasoline-powered cars due to cheaper production costs.
What advancements in technology have helped improve electric cars?
Advancements in battery technology, charging infrastructure, and regenerative braking systems have all helped improve the efficiency and practicality of electric cars.