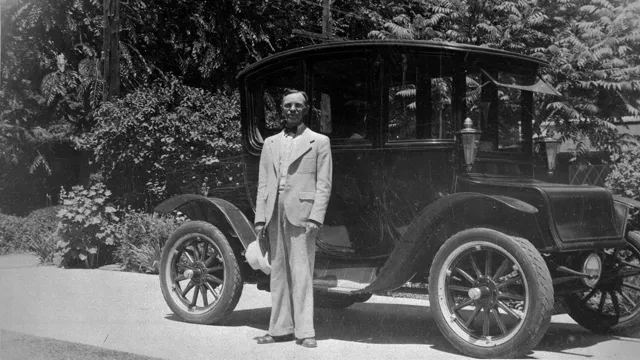The Electrifying Evolution: Tracing the Fascinating History of Electric Cars
Electric cars are becoming increasingly popular in today’s world as people are looking for more environmentally friendly options. However, the history of electric cars dates back to almost two centuries ago. From the invention of the first electric car in the early 1800s to the current advancements in electric car technology, the evolution of electric cars has been nothing short of remarkable.
The first electric car was invented by a Scottish inventor named Robert Anderson in the early 1800s. However, it wasn’t until the late 1800s that electric cars started gaining popularity, mainly due to the invention of rechargeable batteries. By the turn of the 20th century, electric cars were more popular than gasoline-powered cars, with brands such as Columbia and Baker Electric leading the market.
However, the invention of the internal combustion engine and the discovery of abundant, cheap oil reserves shifted the focus to gasoline-powered cars, and electric cars took a back seat. It wasn’t until the 1970s oil crisis that electric cars started making a comeback, with companies such as General Motors, Ford, and Chrysler introducing electric cars as an alternative to gasoline-powered cars. Today, electric car technology has advanced significantly, with companies such as Tesla, Nissan, and Toyota leading the market.
With increasing concerns about climate change and the need for sustainable energy sources, electric cars are poised for a bright future. Join me as we delve into the fascinating history of electric cars and discover how they evolved to become what they are today.
Early Beginnings
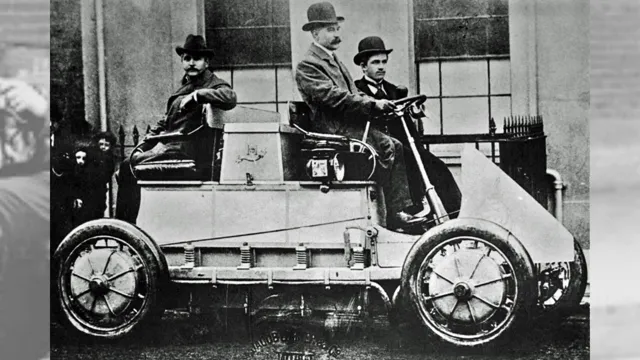
The history of electric cars dates back to the late 19th century when inventors such as Thomas Parker started experimenting with electric vehicles. However, it wasn’t until the early 20th century that electric vehicles started to gain popularity, particularly in urban areas where their quiet operation and lack of exhaust emissions made them a desirable mode of transportation. Electric cars even held various land speed records during this time, with Louis Chevrolet himself piloting the “Flash” to a top speed of 76 mph in 190
However, the rise of gasoline-powered vehicles ultimately overshadowed electric cars, and it wasn’t until the 21st century that electric vehicles started to make a significant comeback. Today, electric cars are seen as a vital component in the transition towards a zero-emissions future, with advancements in battery technology and infrastructure helping to make electric cars a more viable option for more people.
Invention of the Electric Motor
The invention of the electric motor can be traced back to the early 1800s, with the work of pioneers such as Michael Faraday and Joseph Henry. Faraday, in particular, made significant contributions to the field through his groundbreaking experiments on electromagnetic induction. By passing a current through a wire, he was able to create a magnetic field, which in turn produced movement in nearby objects.
This was the foundation for the development of the electric motor, which would go on to revolutionize industry and transportation. However, it wasn’t until the mid-19th century that practical electric motors were developed, thanks to the work of inventors such as Thomas Davenport and Werner Siemens. These early motors were used primarily for small-scale applications, such as powering model trains and telegraph machines, but they paved the way for the widespread adoption of electric power in the coming decades.

First Electric Vehicles
The first electric vehicles may seem like a modern invention, but their origins actually date back to the 19th century. In 1832, Scottish inventor Robert Anderson created the first electric carriage, known as the “Cruise of Glasgow”. However, it wasn’t until the 1880s that electric cars really began to take off, with patents from inventors like Thomas Parker and Magnus Volk.
These early electric cars were often preferred over their gasoline counterparts due to their quietness and lack of emissions. However, their limited range and high cost prevented them from becoming widely adopted. In fact, it wasn’t until the 20th century that electric cars started to gain popularity again, with the development of more advanced battery technology.
It’s interesting to think about how our transportation history could have looked different if these early electric vehicles had caught on more widely.
Decline of Electric Cars
Electric cars have a long and fascinating history that may come as a surprise to many. The initial development of electric vehicles dates back to the late 19th century when a variety of early electric cars were introduced to the market. These cars were quite popular, and their demand continued to grow.
But the high cost of batteries at that time made them expensive and inaccessible to the general public. As the years went by, the popularity of electric cars began to decline, and this was due to the rise of the internal combustion engine and the increasing availability of cheap gasoline. By the mid-twentieth century, gasoline-powered cars had become much more popular, and electric vehicles were seen as old-fashioned and less practical.
However, in recent years, with the increasing focus on environmental issues and the rise of new technologies, electric cars are making a comeback. Modern electric cars are much more efficient and affordable than their early counterparts, and they’re getting more popular with each passing year. Today, many car manufacturers are investing heavily in electric car technology, and it’s clear that the future of the auto industry will be electric.
Introduction of Gasoline-powered Cars
With the introduction of gasoline-powered cars in the early 20th century, electric cars started to disappear from roads. Gasoline-powered cars became popular due to their convenience and reliability, as well as the abundance of gasoline availability. However, the decline of electric cars didn’t happen overnight.
In fact, electric cars were once considered the future of transportation, and several automobile manufacturers produced them in the early 1900s. Electric cars had several benefits, including lower maintenance costs and zero emissions. Unfortunately, the technology of the time prevented the electric cars from reaching the level of performance and range that gasoline-powered cars had, leading to their eventual decline.
While electric cars have made a comeback with modern technology advancements, it’s essential to recognize their early beginnings and why they never took off.
Higher Production Costs of Electric Cars
The higher production costs of electric cars have contributed to the decline in their popularity. Despite their numerous environmental benefits, electric vehicles are still more expensive to manufacture than traditional gas-powered cars. This is due in part to the expensive batteries needed to power the cars.
Additionally, electric cars require specialized parts and equipment that are not commonly used in traditional cars. All of these factors add up to higher production costs, which are ultimately passed on to the consumer in the form of a higher purchase price. As a result, many people are choosing to stick with their gas-powered cars, which are generally more affordable and easier to maintain.
However, as technology advances and more manufacturers begin to produce electric cars, we may see a decline in production costs, making these vehicles a more feasible option for the average consumer.
Revival of Electric Cars
Electric cars have been around since the late 1800s, but it wasn’t until the mid-2000s that they started to make a comeback. In the early days of automobiles, electric cars were actually more popular than gas-powered ones since they were easier to drive and required less maintenance. However, as gas became more readily available and technology improved, electric cars fell out of favor.
Fast forward to the 21st century, and concerns about climate change and the high price of gasoline sparked renewed interest in electric cars. Major automakers such as Tesla, Nissan, and Chevrolet began producing electric cars that were not only eco-friendly but also modern and stylish. Today, electric cars are more popular than ever, with many countries around the world setting ambitious targets for phasing out gas-powered vehicles altogether in the coming years.
While the history of electric cars may be long and checkered, their revival is a testament to the power of innovation and the human desire to reduce our impact on the planet.
Rising Oil Prices and Environmental Concerns
With oil prices on the rise and environmental concerns at an all-time high, it’s no wonder that electric cars have experienced a significant revival over the past decade. Today, we are witnessing the dawn of a new era where consumers are increasingly opting for eco-friendly vehicles that not only save them money in the long run but also help preserve the planet. Electric cars, powered by electric motors, run on rechargeable batteries, offering a clean and sustainable alternative to gasoline cars.
They emit zero emissions and are significantly more energy-efficient, making them the go-to choice for those looking to make a positive impact on the environment. The best part? With advances in technology, electric cars can now last for hundreds of miles on a single charge, making them a viable option for daily use. As we move towards a greener future, electric cars are set to play a pivotal role in reducing our carbon footprint and ensuring a sustainable future for generations to come.
Introduction of Hybrid Vehicles
Hybrid vehicles have quickly become a popular alternative to traditional gasoline-powered cars. One of the factors driving the increase in hybrid cars is the revival of electric cars. With concerns over the environment and rising gas prices, more and more people are looking for cars that are eco-friendly and cost-effective.
Electric cars, in particular, have been receiving a lot of attention in recent years, and many automakers are investing in developing them. The use of electric motors and batteries in hybrid vehicles has allowed them to become more efficient and environmentally friendly while still offering the convenience of a traditional fuel-powered car. With increasing demand, the development of electric and hybrid vehicles is sure to continue.
Current State of Electric Cars
The history of electric cars dates back to the mid-19th century when inventors started to experiment with battery-powered vehicles. However, it was in the 20th century that electric cars became more popular due to concerns over the environmental impact of gasoline-fueled cars and the continuous improvements in battery technology. The early 2000s saw the introduction of the first modern electric car, the Tesla Roadster, which was widely acclaimed for its impressive performance and range.
Since then, the electric car market has continued to grow, with more manufacturers introducing their own models and governments worldwide offering incentives to promote electric car adoption. Currently, electric cars are seen as a viable alternative to traditional gas-powered cars, with their increasing popularity and advancements in battery technology making them more affordable and practical. As the world shifts towards cleaner, greener energy solutions, it is expected that electric cars will play a crucial role in the future of transportation.
Advancements in Battery Technology
Electric cars have come a long way over the past few years, thanks in large part to advancements in battery technology. While earlier electric car models suffered from limited driving range, modern electric vehicles can travel impressive distances without needing a recharge. However, the current state of electric cars is still far from perfect.
While the range has improved significantly, it can still be a concern for long road trips. Additionally, the overall cost of electric cars remains high, putting them out of reach for many consumers. Nevertheless, with ongoing developments in battery technology, it’s likely that we’ll continue to see improvements in the range, performance, and affordability of electric vehicles in the years to come.
As these advancements are adopted more widely, we may be on the brink of a transportation revolution.
Government Support and Incentives
Electric cars have come a long way since their inception, and the current state of the market is very promising. Governments around the world are offering a wide range of incentives and support for electric cars to help encourage their adoption. These incentives can include things like tax credits, rebates, and reduced tolls and parking fees.
Additionally, many governments are investing in charging infrastructure to make it easier for electric car owners to find a place to charge their vehicles. All of this government support has helped to make electric cars more affordable and more accessible to the average person. As a result, more and more people are making the switch to electric cars, and the market share of electric vehicles is growing rapidly.
This trend is expected to continue in the coming years as more people become aware of the benefits of electric cars and as the technology continues to improve.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the history of electric cars can be summarized as a rollercoaster ride of innovation, setbacks, and occasional surges in popularity. From humble beginnings in the 19th century to the dominance of gasoline-powered cars in the 20th century and the recent resurgence of interest in electric vehicles, the journey of electric cars proves that the road to sustainable transportation is paved with challenges and unexpected turns. Nevertheless, the ingenuity and determination of engineers, entrepreneurs, and environmentalists continue to drive the electric car revolution forward, providing us with a glimpse of a greener and brighter automotive future.
So, let’s buckle up and enjoy the ride!”
FAQs
When were the first electric cars invented?
The first electric car was invented in 1837 by Scottish chemist Robert Anderson.
What is the range of an average electric car?
The range of an average electric car is around 100-200 miles on a single charge, depending on the make and model.
How have electric cars evolved over time?
Electric cars have evolved significantly since their invention in the 19th century, with advancements in battery technology, motor efficiency, and overall driving range. Today, electric cars are becoming more popular due to their reduced emissions and improved performance.
How long does it take to charge an electric car?
The time it takes to charge an electric car depends on the make and model, as well as the type of charger used. On average, it can take anywhere from 30 minutes to several hours to fully charge an electric car. Some cars also have the option to quick-charge for faster charging times.