Who Makes Fords Electric Car Batteries Revealed

Featured image for who makes ford’s electric car batteries
Image source: electriccarwiki.com
Ford partners with SK Innovation and LG Energy Solution to manufacture its electric car batteries, leveraging cutting-edge technology for models like the F-150 Lightning and Mustang Mach-E. These global leaders in battery production ensure high performance, reliability, and scalability as Ford accelerates its EV ambitions.
Key Takeaways
- Ford partners with SK Innovation: Primary battery supplier for U.S.-made EVs like the F-150 Lightning.
- New BlueOval SK joint venture: Ford and SK build U.S. battery plants for future EV production.
- LFP batteries coming soon: Ford adopts lower-cost, longer-life LFP tech for select models by 2026.
- Global supply chain: Batteries sourced from SK’s Georgia and Tennessee plants, ensuring domestic production.
- Vertical integration strategy: Ford invests in raw materials to secure long-term battery supply stability.
📑 Table of Contents
- The Electric Revolution: Ford’s Battery Power Uncovered
- Ford’s Battery Strategy: A Blend of Partnerships and In-House Innovation
- Key Partners: Who Actually Builds Ford’s Electric Car Batteries?
- Ford’s In-House Battery Development: The Road to Self-Reliance
- Battery Types and Technologies: What Powers Ford’s EVs?
- Challenges and the Road Ahead
- Conclusion: Who Makes Ford’s Electric Car Batteries? The Full Picture
The Electric Revolution: Ford’s Battery Power Uncovered
Remember when electric cars were a distant dream, something we saw only in sci-fi movies? Fast forward to today, and they’re zipping past us on highways, parked in driveways, and even becoming the talk of the town. Among the frontrunners in this electrifying race is Ford, an American automotive giant that’s been shifting gears—quite literally—into the electric era. But have you ever wondered, who makes Ford’s electric car batteries? It’s not just about the car itself; it’s about the powerhouse beneath the hood that drives the future.
As someone who’s always been curious about how things work—especially when it comes to tech and sustainability—I dove deep into Ford’s electric vehicle (EV) journey. I wanted to know not just who’s behind the battery tech, but how Ford is positioning itself in a competitive, fast-evolving market. Whether you’re an EV enthusiast, a potential buyer, or just someone who likes knowing the “how” behind the headlines, this deep dive will answer your questions. We’ll explore Ford’s partnerships, in-house developments, and the real-world implications of their battery choices. So, let’s pop the hood and see what’s powering Ford’s electric dreams.
Ford’s Battery Strategy: A Blend of Partnerships and In-House Innovation
From Outsourcing to Strategic Collaboration
When Ford first dipped its toes into the electric vehicle market, it relied heavily on third-party battery suppliers—a common approach for automakers transitioning into EVs. But as demand for EVs grew and competition intensified (think Tesla, GM, and even tech companies entering the space), Ford realized it needed more control over its supply chain. That’s when the shift from simple outsourcing to strategic partnerships and in-house development began.
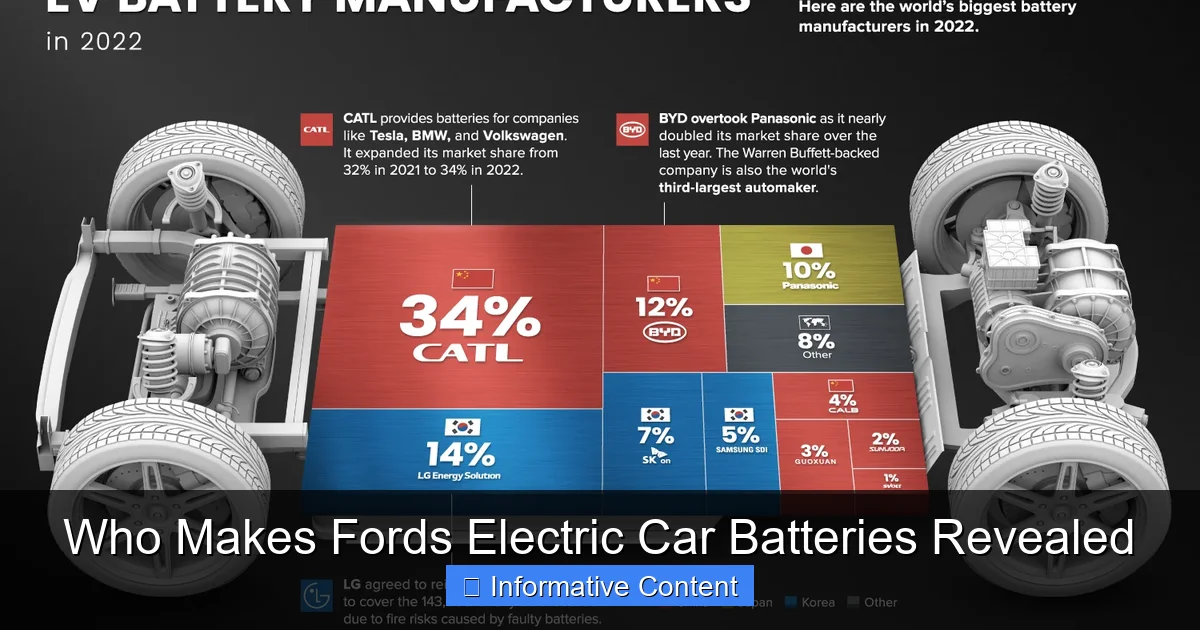
Visual guide about who makes ford’s electric car batteries
Image source: visualcapitalist.com
Unlike some automakers that still rely solely on external suppliers, Ford is taking a hybrid approach. It’s not just buying batteries off the shelf; it’s investing in joint ventures, building its own battery plants, and even developing new battery chemistries. This strategy ensures better quality control, faster innovation, and reduced dependency on global supply chains—something that became crucial during recent chip and battery material shortages.
Why Battery Ownership Matters
Imagine you’re building a house. You could hire a contractor to source all the materials, or you could own the lumber mill, the glass factory, and the concrete plant. The second option gives you more control, lower long-term costs, and the ability to customize. That’s exactly what Ford is doing with batteries.
Owning battery production allows Ford to:
- Improve vehicle range by optimizing battery packs for specific models like the F-150 Lightning or Mustang Mach-E.
- Reduce costs over time by cutting out middlemen and scaling production.
- Enhance sustainability by managing recycling and reuse programs in-house.
- Speed up innovation by aligning battery development with vehicle design from day one.
For example, Ford’s decision to build the BlueOval SK battery plant in Kentucky wasn’t just about capacity—it was about creating a direct line between battery R&D and vehicle manufacturing. This kind of integration is a game-changer.
Key Partners: Who Actually Builds Ford’s Electric Car Batteries?
SK On: The Powerhouse Behind BlueOval SK
The biggest name in Ford’s battery story is SK On, a South Korean battery manufacturer and a subsidiary of SK Group. SK On is one of the world’s top three EV battery producers and has been a critical partner for Ford since 2021. Together, they formed BlueOval SK, a joint venture with a staggering $11.4 billion investment.
BlueOval SK operates three massive battery plants:
- Kentucky 1 (Glendale): 43 GWh annual capacity
- Kentucky 2 (Glendale): 43 GWh annual capacity
- Tennessee (Stanton): 43 GWh annual capacity
That’s a total of 129 GWh per year—enough to power over 1.5 million EVs annually. These plants supply batteries for the F-150 Lightning, Mustang Mach-E, and future electric models. SK On brings cutting-edge NMC (Nickel Manganese Cobalt) battery tech, known for high energy density and fast charging—perfect for Ford’s rugged, performance-oriented EVs.
LG Energy Solution: A Longtime Ally
Before SK On, Ford’s main battery partner was LG Energy Solution, another South Korean giant. LG supplied batteries for early Ford EVs like the Focus Electric and played a key role in the Mustang Mach-E’s launch. Even today, LG continues to supply batteries for certain Ford models, especially in North America and Europe.
LG’s batteries use a mix of NMC and LMO (Lithium Manganese Oxide) chemistries, balancing energy density, thermal stability, and cost. While Ford is shifting more production to BlueOval SK, LG remains a trusted partner—especially for models that require flexible, modular battery packs.
CATL: The Chinese Connection
Here’s a twist: Ford has also partnered with Contemporary Amperex Technology Co. Limited (CATL), the world’s largest battery manufacturer. In 2023, Ford announced a licensing deal with CATL to produce LFP (Lithium Iron Phosphate) batteries at a new plant in Michigan.
Why LFP? Because it’s:
- Cheaper than NMC
- Safer (less risk of thermal runaway)
- More durable (longer cycle life)
- Free from cobalt and nickel (more ethical sourcing)
This partnership is a smart move. LFP batteries won’t power high-performance models like the Mach-E GT, but they’re perfect for base models and fleet vehicles (think delivery vans, taxis, and commuter cars). Ford gets cost savings and sustainability benefits, while CATL gains a foothold in the U.S. market without direct competition.
Ford’s In-House Battery Development: The Road to Self-Reliance
Ford Ion Park: Where Innovation Happens
Ford isn’t just relying on partners—it’s building its own battery expertise. In 2021, Ford opened Ford Ion Park in Romulus, Michigan, a $185 million R&D hub dedicated to battery tech. Think of it as Ford’s “battery lab,” where engineers and scientists work on everything from chemistry to recycling.
At Ion Park, Ford focuses on:
- New battery chemistries (like solid-state and sodium-ion)
- Cell design and packaging (to fit Ford’s unique vehicle architectures)
- Thermal management (to prevent overheating in cold weather)
- Recycling and second-life applications (repurposing old batteries for energy storage)
For example, Ford recently tested a new “tabless” battery design that reduces heat and increases charging speed. If successful, this could be a major breakthrough for future EVs.
Solid-State Batteries: The Next Frontier
While current Ford EVs use lithium-ion batteries, the company is actively researching solid-state batteries—the holy grail of EV tech. Solid-state batteries replace liquid electrolytes with solid ones, offering:
- Higher energy density (longer range)
- Faster charging (minutes vs. hours)
- Improved safety (no risk of leaks or fires)
- Longer lifespan (thousands of cycles)
Ford has invested in several startups, including Solid Power, a Colorado-based company developing sulfide-based solid-state batteries. In 2023, Ford began testing Solid Power’s prototypes in the F-150 Lightning. While commercial use is still a few years away, this research shows Ford’s commitment to staying ahead of the curve.
Battery Types and Technologies: What Powers Ford’s EVs?
NMC vs. LFP: The Chemistry Breakdown
Not all batteries are created equal. Ford uses two main chemistries: NMC (Nickel Manganese Cobalt) and LFP (Lithium Iron Phosphate). Here’s how they compare:
| Feature | NMC (e.g., Mustang Mach-E) | LFP (e.g., F-150 Lightning Standard Range) |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Density | High (up to 700 Wh/L) | Moderate (up to 500 Wh/L) |
| Range | Longer (up to 300+ miles) | Shorter (up to 240 miles) |
| Cost | Higher (cobalt/nickel expensive) | Lower (iron phosphate is cheap) |
| Lifespan | 8–10 years | 10–15 years |
| Charging Speed | Faster (DC fast charge) | Slower (but improving) |
| Thermal Safety | Moderate | Excellent (no cobalt, less flammable) |
| Best For | Performance models, long-range EVs | Budget models, fleet vehicles |
Ford’s strategy? Use NMC for high-end models where range and speed matter, and LFP for affordable, high-volume vehicles. This “dual chemistry” approach maximizes value across the lineup.
Modular Battery Packs: Flexibility is Key
Another innovation is Ford’s modular battery packs. Instead of one fixed battery size, Ford designs packs that can be stacked or reconfigured. For example:
- The F-150 Lightning comes with two battery options: Standard (98 kWh) and Extended Range (131 kWh). The same chassis, different pack sizes.
- The E-Transit van uses modular packs to fit different wheelbase lengths and payloads.
This flexibility saves money, simplifies manufacturing, and lets customers choose the range they need—without overpaying for unused capacity.
Challenges and the Road Ahead
Supply Chain Hurdles: Raw Materials and Geopolitics
Even with strong partners, Ford faces challenges. EV batteries require rare materials like lithium, cobalt, and nickel—and these come with risks:
- Price volatility: Lithium prices spiked 400% in 2022.
- Geopolitical tensions: 70% of cobalt comes from the Democratic Republic of Congo, where mining practices raise ethical concerns.
- Logistics delays: Shipping battery cells across oceans isn’t foolproof.
To address this, Ford is:
- Investing in recycling programs to recover materials from old batteries.
- Partnering with U.S. mines (e.g., in Nevada and North Carolina) to source lithium locally.
- Reducing cobalt use in new batteries (e.g., LFP and low-cobalt NMC).
Competition: Can Ford Keep Up?
Tesla, GM, and Hyundai are all investing heavily in batteries. GM’s Ultium platform, for example, promises 400-mile ranges and 10-minute charging. Ford’s response? Speed up its own innovation.
- Ford Pro: A new division focused on commercial EVs, using LFP batteries for cost savings.
- Ford Model e: A separate EV unit to accelerate R&D and software integration.
- Global expansion: Building battery plants in Europe and China to serve local markets.
The race is on, but Ford’s mix of partnerships, in-house tech, and strategic flexibility gives it a fighting chance.
Conclusion: Who Makes Ford’s Electric Car Batteries? The Full Picture
So, who makes Ford’s electric car batteries? The answer isn’t one company—it’s a strategic ecosystem of partners, joint ventures, and in-house innovation. SK On and LG Energy Solution supply high-performance NMC batteries, CATL brings cost-effective LFP tech, and Ford Ion Park drives the future with solid-state research.
This hybrid model—outsourcing where it makes sense, owning where it matters—is Ford’s secret weapon. It’s not just about who builds the batteries; it’s about how Ford integrates them into a broader vision: affordable, sustainable, and high-performance EVs for everyone.
As someone who’s watched the EV market evolve, I’m impressed by Ford’s ambition. They’re not just catching up to Tesla—they’re carving their own path. Whether you’re eyeing an F-150 Lightning for work or a Mustang Mach-E for fun, knowing that Ford controls its battery destiny adds peace of mind. After all, when the battery’s reliable, the ride is electric—in every sense of the word.
The next time you see a Ford EV on the road, remember: beneath the sleek body and roaring silence, there’s a network of innovators, engineers, and partners powering the future. And that’s a story worth driving home.
Frequently Asked Questions
Who makes Ford’s electric car batteries?
Ford partners with major battery manufacturers like SK Innovation (now SK On) and LG Energy Solution to produce its electric car batteries. These companies supply lithium-ion battery cells for models like the Mustang Mach-E and F-150 Lightning.
Where are Ford’s electric car batteries made?
Ford’s batteries are produced in facilities across the U.S. and globally, including SK Innovation’s Georgia plant and LG Energy Solution’s Michigan factory. The automaker is also investing in domestic battery plants to support its EV expansion.
Does Ford make its own electric car batteries?
Ford doesn’t manufacture battery cells in-house but designs and assembles battery packs at its own facilities, like the Rouge Electric Vehicle Center. The company relies on third-party suppliers for raw materials and cell production.
Which companies supply Ford with electric car batteries?
Key suppliers include SK On (a division of SK Innovation) and LG Energy Solution, which provide high-performance battery cells for Ford’s EVs. Ford is also building a joint-venture battery plant with SK On in Kentucky.
Are Ford’s electric car batteries made in the USA?
Many of Ford’s batteries are produced in the U.S., with SK On and LG Energy Solution operating domestic plants. Ford aims to further localize production with upcoming facilities, like the BlueOval SK hub in Tennessee.
What type of batteries does Ford use in its electric cars?
Ford uses lithium-ion batteries with nickel-manganese-cobalt (NMC) chemistry for most EVs, supplied by SK On and LG Energy Solution. The company is also developing solid-state battery technology for future models.





